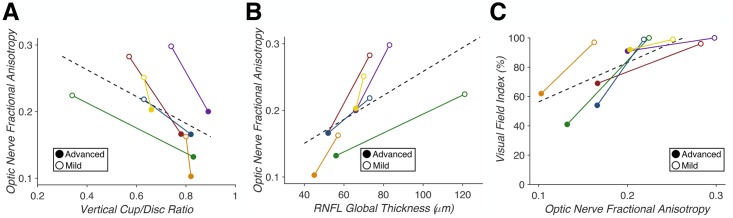
Fig 6. Correlation of dMRI fractional anisotropy with clinical measures of glaucoma (n = 6).
(A) Vertical cup-to-disc ratio predicts optic nerve fractional anisotropy (p = 0.0077, R2 = 0.66). (B) Average retinal nerve fiber layer thickness predicts optic nerve fractional anisotropy (p = 0.0069, R2 = 0.63). (C) Optic nerve fractional anisotropy predicts visual field index (p = 0.0029, R2 = 0.52). Correlations within individual patients are indicated by each solid colored line, with closed points marking eyes with “advanced” glaucoma and open points marking eyes with “mild” glaucoma. A least-squares regression estimate is indicated by the dashed line.