Figure 4. RNAseq analysis demonstrates that HDAC5AA overexpression regulates pathways related to mTOR.
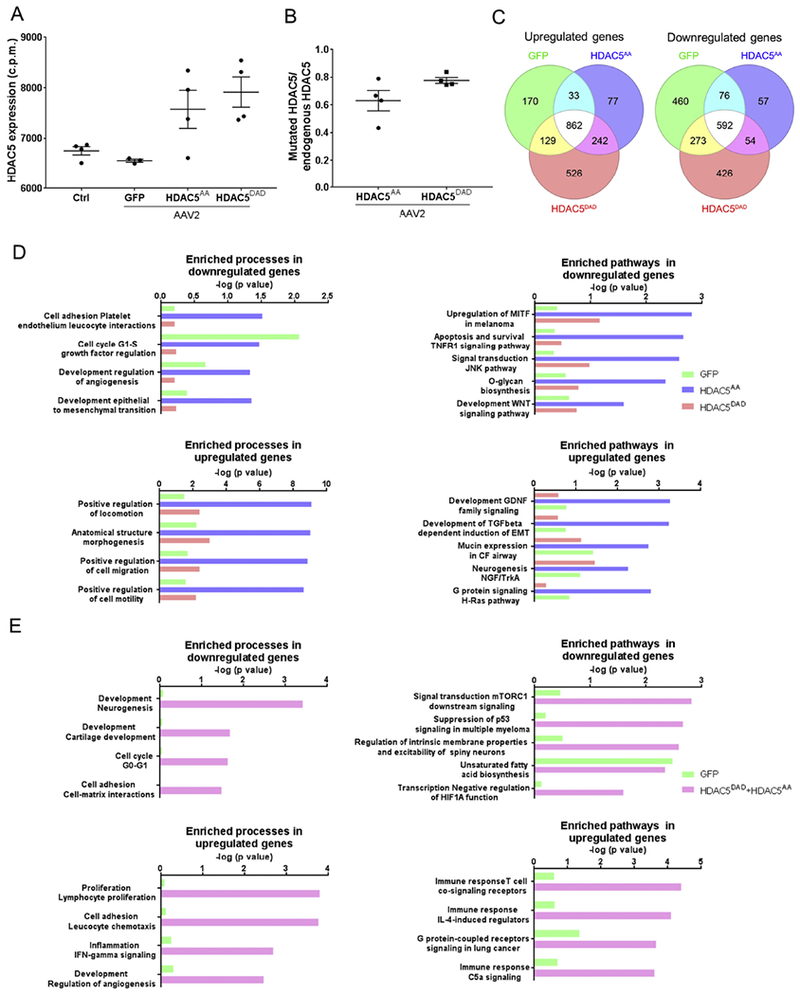
(A) Retinas were intravitreally injected with either AAV2-GFP, AAV2-FLAG-HDAC5AA or AAV2-FLAG-HDAC5DAD. 15 days later, optic nerve injury was performed. 4 days after optic nerve injury, retinas were processed for RNAseq. Control refers to non-injected, non-injured retina. N=4. HDAC5 mRNA expression levels in counts per million (c.p.m) of HDAC5 in the different conditions. (B) Ratio between the number of reads of HDAC5 mutants at the DNA location of serine 498 and number of reads in the homologous region in the endogenous HDAC5. Plotted values in (A) and (B)were quantified and expressed as mean ± SEM. (C) Venn diagram indicating the number of differentially expressed genes in each condition compared to the non-injected, non-injured control retina. (D) Enriched processes and pathways in the set of genes that are differentially expressed in retinas overexpressing GFP, HDAC5AA or HDAC5DAD. (E) Enriched processes and pathways in the set of genes that are differentially expressed in retinas overexpressing GFP compared to both HDAC5AA and HDAC5DAD.
