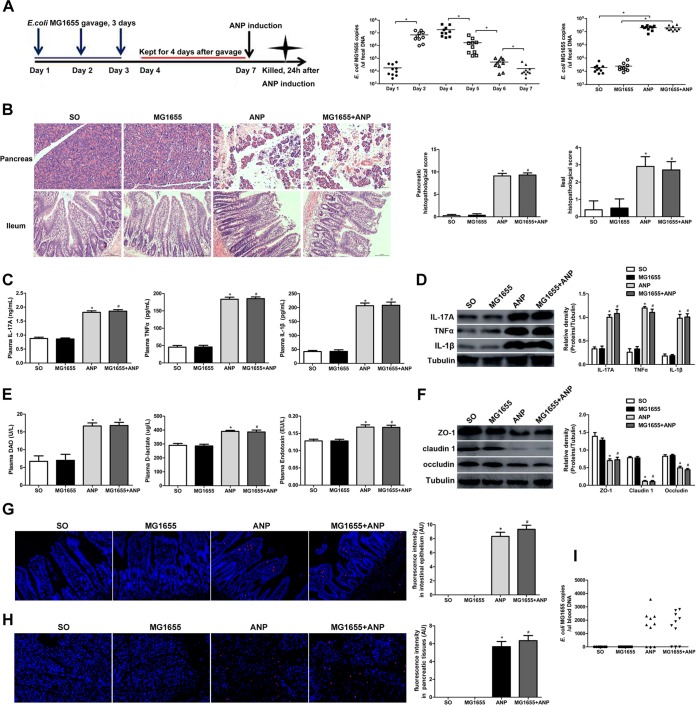
FIG 4.
Administration of E. coli MG1655 by gavage to conventional rats showed no effects on the pancreas and ileum. (A) Time axis of E. coli MG1655 administration by gavage and ANP induction in conventional rats and quantity of fecal E. coli MG1655 as determined by qPCR. *, P < 0.05. (B) Histological analysis of the pancreas and ileum (H&E, ×200). (C) IL-17A, TNF-α, and IL-1β levels in the plasma as determined by ELISA. (D) IL-17A, TNF-α, and IL-1β expression in the ileum as determined by Western blotting. (E) DAO, d-lactate, and endotoxin levels in the plasma. (F) ZO-1, claudin 1, and occludin expression in the ileum as determined by Western blotting. (G and H) Gut bacterial translocation to the intestinal epithelia (G) and the pancreas (H) as determined by FISH using a probe of E. coli (red represents E. coli, and blue represents nuclei). (I) E. coli MG1655 DNA detection in peripheral blood as determined by qPCR. n = 10 per group. Three independent experiments were performed. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni’s posttest. *, P < 0.05 versus the SO group; #, P < 0.05 versus the ANP group. SO, sham operated.