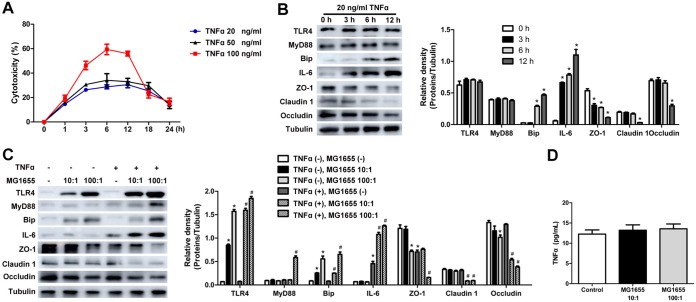
FIG 7.
E. coli MG1655 increased TNF-α-induced intestinal epithelial cell injury in vitro. (A) Cytotoxicity of 20-, 50-, and 100-ng/ml TNF-α treatments of IEC-18 cells. (B) TLR4, MyD88, Bip, IL-6, ZO-1, claudin 1, and occludin levels as determined by Western blotting in IEC-18 cells incubated with 20 ng/ml TNF-α for 3, 6, and 12 h. *, P < 0.05 versus the 0-h group. (C) TLR4, MyD88, Bip, IL-6, ZO-1, claudin 1, and occludin levels as determined by Western blotting in IEC-18 cells challenged with TNF-α and E. coli MG1655 in combination. (D) TNF-α level in the culture supernatant as determined by ELISA. The control represents IEC-18 cells without MG1655 addition. Three independent experiments were performed. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni’s posttest. *, P < 0.05 versus the control group without TNF-α and MG1655 intervention; #, P < 0.05 versus the TNF-α group.