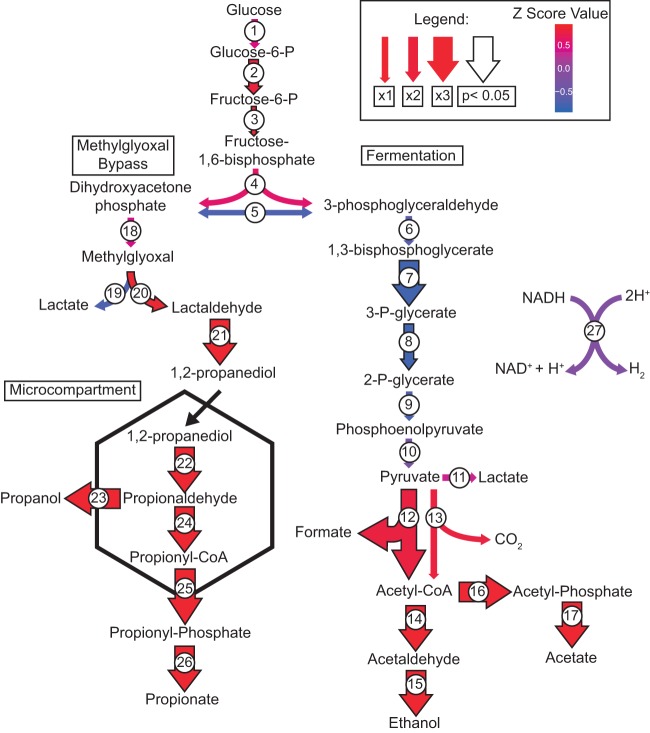
FIG 3.
Predicted carbon flux through H. congolense WG8 when grown under pressure (21, 35, and 48 MPa) using proteomic and NMR analyses. H. congolense WG8 is a strict fermenter, and glucose was the substrate provided during growth experiments. Major fermentation products are acetate, ethanol, formate, lactate, propanol, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen gas (only when grown at 0.1 MPa). The production of 1,2 propanediol is hypothesized to be a result of the methylglyoxal bypass, which may become important during high-pressure growth because activity of triose phosphate isomerase (protein 5) decreases under pressure. 1,2-Propanediol and other alcohols converted into aldehydes are processed in a microcompartment to contain toxic aldehyde intermediates. The arrow size represents the increased abundance of a protein under 1, 2, or 3 high-pressure growth conditions. Arrows outlined in black represent statistically significant changes in protein abundance (P < 0.05). Arrow colors are based on Z-score values calculated from protein abundances. Proteins: 1, phosphotransferase; 2, glucose-6-phosphate isomerase; 3, phosphofructokinase; 4, fructose bisphosphate aldolase; 5, triose phosphate isomerase; 6, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; 7, 3-phosphoglycerate kinase; 8, phosphoglycerate mutase; 9, enolase; 10, pyruvate kinase; 11, lactate dehydrogenase; 12, pyruvate formate lyase; 13, pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase; 14, aldehyde dehydrogenase; 15, alcohol dehydrogenase; 16, phosphotransacetylase; 17, acetate kinase. Methyl glyoxal bypass: 18, methylglyoxal synthase; 19, glyoxalase; 20, methylglyoxal reductase; 21, 1,2-propanediol dehydrogenase. Microcompartment: 22, propanediol dehydratase; 23, alcohol dehydrogenase; 24, propionaldehyde dehydrogenase; 25, phosphotransacetylase; 26, propionate kinase; 27, hydrogenase.