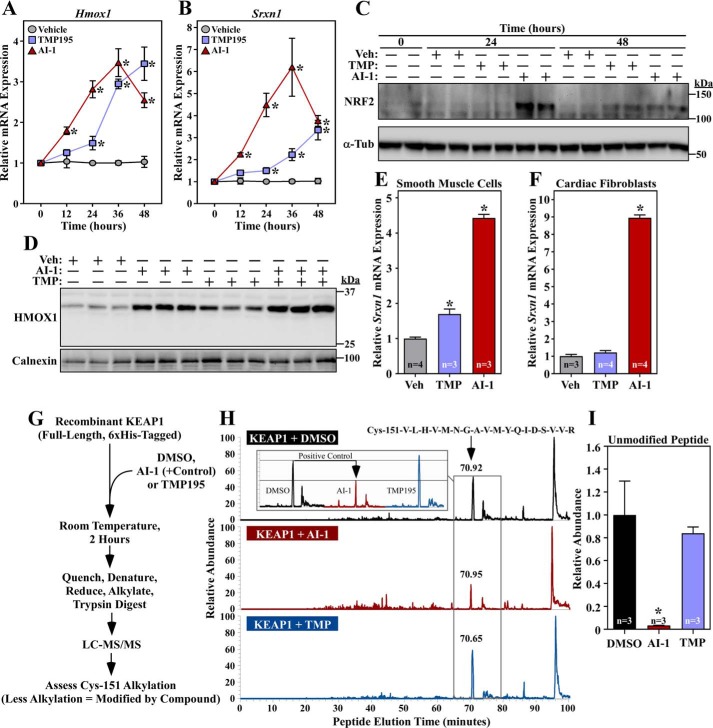
Figure 5.
Class IIa HDAC catalytic domain inhibition does not stimulate NRF2 through KEAP1 inactivation. A and B, NRVMs were treated with vehicle control (DMSO, 0.1% final concentration), TMP195 (3 μm), or AI-1 (10 μm) for the indicated times. Hmox1 (A) and Srxn1 (B) mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR. Values represent means + S.E.; n = plates of cells/condition. *, p < 0.05 versus vehicle at the equivalent time. C, protein homogenates were prepared from NRVMs treated as described in A and subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies specific for NRF2 or α-tubulin (α-Tub). Veh, vehicle. D, NRVMs were treated for 36 h with compounds and vehicle control as described above. Protein homogenates were immunoblotted with antibodies against HMOX1; calnexin served as a loading control. E and F, primary rat aortic smooth muscle cells (E) and neonatal rat cardiac fibroblasts (F) were treated for 48 h with compounds and vehicle control as described above; Srxn1 mRNA expression was assessed by qRT-PCR. Values represent means + S.E. *, p < 0.05 versus vehicle. G, schematic of the in vitro assay to determine whether TMP195 covalently couples to KEAP1. H, the signals of unmodified tryptic peptides that contain KEAP1 Cys-151, which is a common site of electrophilic addition, were measured on an LTQ IonTrap following in vitro incubation of KEAP1 with vehicle control, TMP195, or AI-1; AI-1 served as a positive control. The LC peaks for the Cys-151–containing peptide are indicated by a black arrow; a reduced signal indicates that a compound conjugated to the peptide. The inset shows a side-by-side comparison of the peak for the Cys-151–containing peptide in the different treatment groups. I, the MS experiment in H was repeated to include three additional samples per treatment group. Relative abundance reflects the area under the curve normalized to the DMSO group. Values represent means + S.E. *, p < 0.05 versus DMSO-treated peptide.