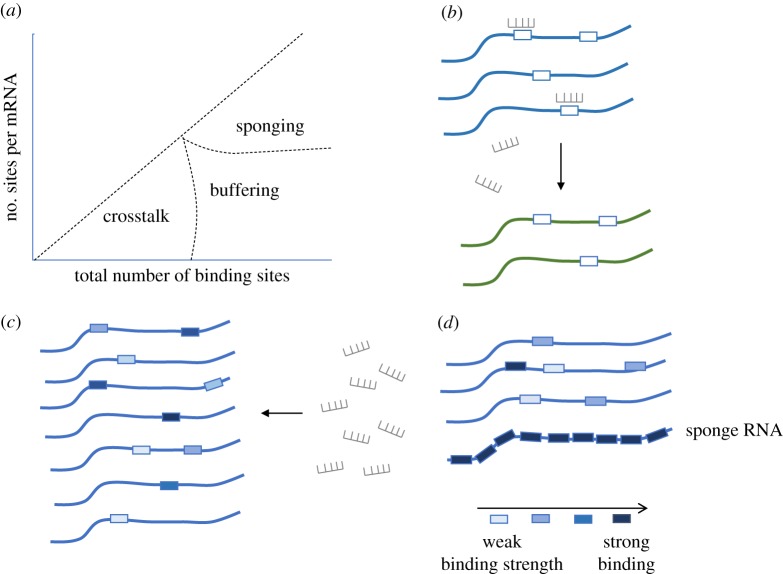
Figure 4.
Types of competition effects between miRNA binding sites. (a) The three regimes based on the relation between the total number of binding sites and the number of miRNA binding sites per mRNA. (b) Low total number of binding sites and a low number of sites per transcripts lead to a regulatory crosstalk between transcripts. In this scenario, certain RNA molecules (blue) can regulate the levels of target transcript (green) by competing for binding to the same miRNA. (c) The buffering effect of miRNAs describes a situation in which the large number of potential binding sites prevents saturation, and thus, allows changes in the concentration of a miRNA to sensitively regulate binding sites with different affinities. (d) The ‘sponge’ effect describes the expression of RNAs with many strong binding sites that can reduce site occupancies by sequestration of miRNAs. (Online version in colour.)