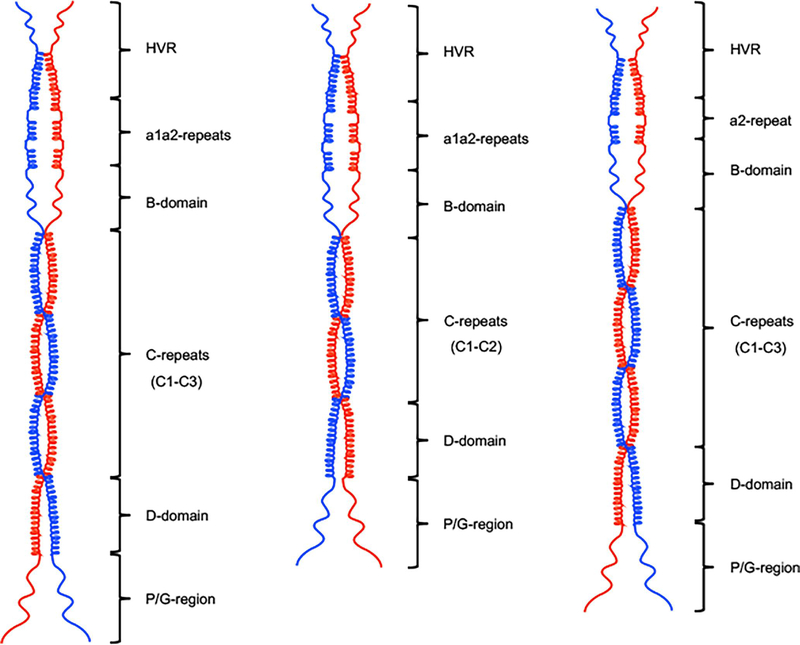
Fig. 8.
The structural model of r-PAMs. Models were drawn to scale in ChemDraw Professional 16.0. According to the results from CD, AUC, and heptad register alignments, the c-repeats of the C-domain, together with partial HVR and D-domain regions, form helical coiled-coil dimers in a rod-like conformation in solution. But a1a2-repeats and most of the B-domain manifest coiled-coil disrupting properties. (A) Class I and III PAMs, except PAMSS1574, encompass three c-repeats and intact a1a2-repeats. (B) PAMSS1574 is the shortest among all naturally occurring PAMs due to the loss of one c-repeat, despite the complete a1a2-repeats as other Class I and III PAMs. (C) Class II PAMs, viz. PAMNS88.2 and PAMSS1448, lack the whole a1-repeat but express three c-repeats. In the C-domain.