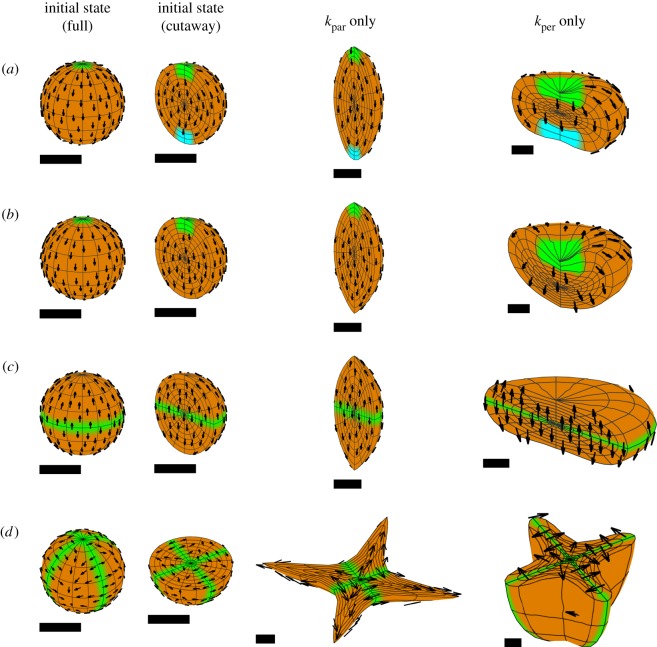
Figure 13.
Anisotropic growth of a sphere. Growth is uniform, and either parallel or perpendicular to POL. (a) POL is created by diffusion between a source (+ORG, green) and a sink (−ORG, cyan) in small regions at opposite poles. Positive kpar creates a pointed ellipsoid. Positive kper creates an indented disc. (b) POL is created by diffusion and decay from a source at the upper pole. Positive kpar gives a pointed ellipsoid. Positive kper gives a cup. (c) POL is produced by a source in an equatorial region, diffuses and decays. Positive kpar gives a pointed ellipsoid. Positive kper gives a flat sheet. (d) POL is produced by two vertical midplanes at right angles to each other. Positive kpar gives a star shape, whose points are in the diagonal directions. Positive kper gives two interpenetrating sheets. The cutaway views here show the lower half of the tissue. The upper half is symmetric. Orange represents the specified growth rate, green +ORG and cyan −ORG. The arrow fields can be more clearly seen under enlargement.