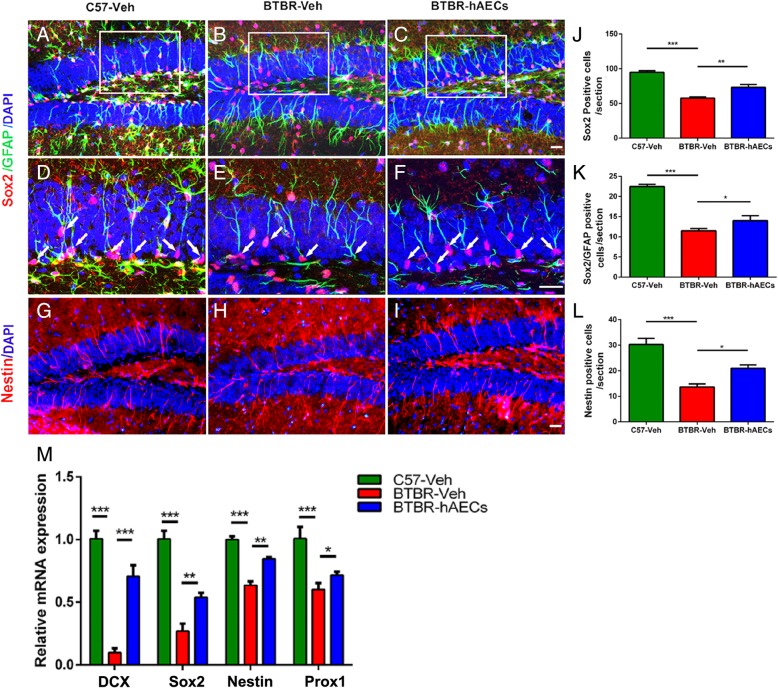
Fig. 5.
hAEC treatment enriched the NPC pool in the DGs and showed molecular beneficial effects in BTBR mice. a–c Representative images of Sox2 and GFAP double-positive RGCs in the DGs. d–f The images are the magnified views in a–c. The arrows indicate the Sox2 and GFAP double-stained cells. g–i Representative images of Nestin-positive RGCs in the DGs. j Quantitative analysis of the numbers of Sox2-positive cells in the DG-SGZ. of Vehicle-treated BTBR mice exhibited less Sox2-positive cells in the DG-SGZ compared to C57 mice, and the number of Sox2-positive cells was increased after hAEC treatment in BTBR mice. k Quantitative analysis of the number of Sox2+/GFAP+ cells in the DG-SGZ. vehicle-treated BTBR mice also exhibited less Sox2+/GFAP+ cells in the DG-SGZ compared to C57 mice, and the number of Sox2+/GFAP+ cells was increased after hAEC treatment in BTBR mice. l Quantitative analysis of the number of Nestin+ cells in the GCL. C57 mice exhibited more Nestin-positive cells in the GCL compared to vehicle-treated mice, and the number of Nestin-positive cells was increased after hAEC treatment in BTBR mice. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 4). i Relative mRNA expressions of DCX, Sox2, Nestin, and Prox1, which are expressed in low levels in BTBR mice treated with vehicle compared to C57 mice but increased after hAEC treatment in BTBR mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. The scale bar in c = 50 μm and applies to a–c; in f = 20 μm and applies to d–f, and in i = 50 μm and applies to g–i