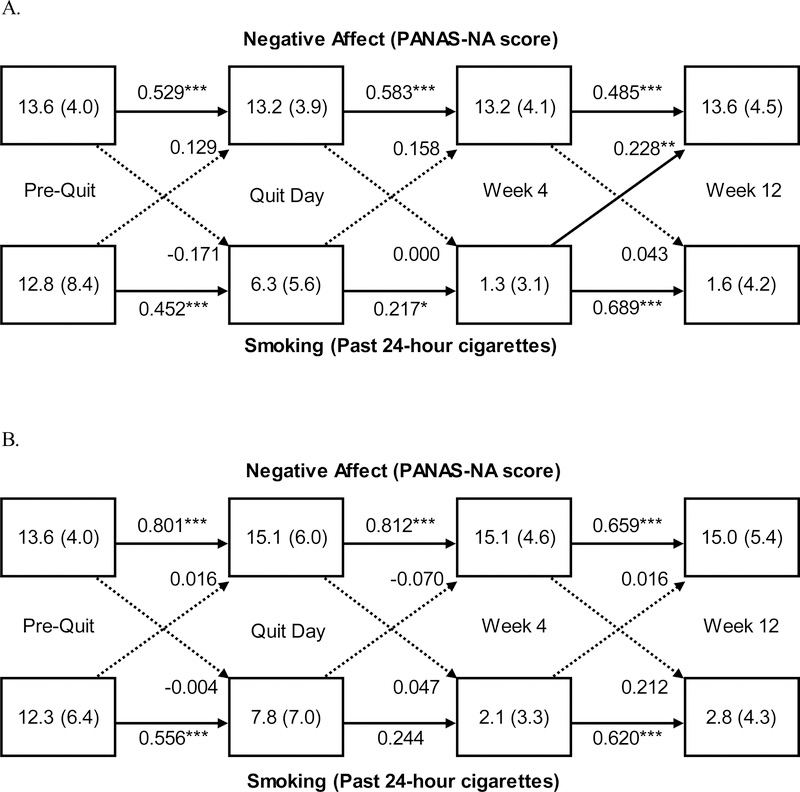
Figure 1.
Panel analysis of negative affect (NA) and smoking among adherent participants (n=96; Panel A) and among nonadherent participants (n=23; Panel B) during the 12-week, open-label phase of a smoking cessation clinical trial using varenicline plus behavior counseling among adults with a cancer diagnosis. Values in the boxes indicate the Mean (Standard Deviation) NA score or smoking level, respectively. Solid lines represent significant path coefficients. Dotted lines represent non-significant path coefficients. Values on the lines represent standardized path coefficients, which indicate the proportion of variance in Y (e.g., TQD NA) that is explained by X (e.g., PQ Smoking). Error covariances of endogenous variables (e.g., PQ NA and PQ Smoking) were included in the model. NA was assessed by the Positive and Negative Affect Scale (PANAS) negative affect score. Smoking was self-reported number of cigarettes smoked in the past 24 hours. *p<.05 **p<.01 ***p<.001