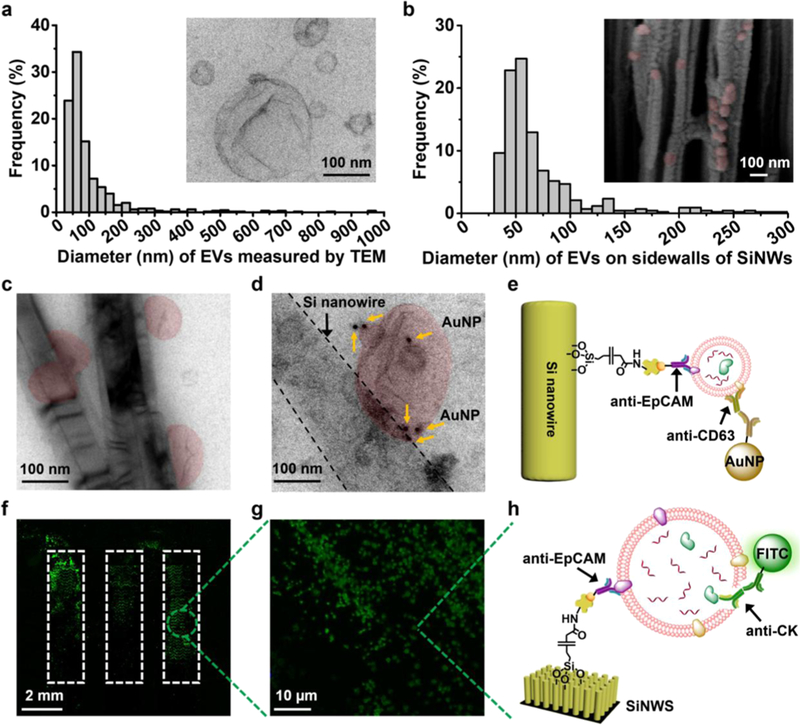
Figure 2.
Characterization of tumor-derived EVs in solution and on anti-epithelial cell adhesion molecule (anti-EpCAM)-grafted silicon nanowire substrates (SiNWSs) in NanoVilli Chips. (a) Size distribution (n = 653, diameters = 30–1000 nm) of HCC78-derived EVs, measured by TEM. Inset: a representative TEM image (scale bar, 100 nm) of HCC78-derived EVs. (b) Size distribution of HCC78-derived EVs (n = 425, diameters = 30–300 nm) immunoaffinity-captured on the sidewalls of Si nanowires (SiNWs) measured by SEM. Inset: a representative cross-sectional SEM image (scale bar, 100 nm) of a device with immobilized HCC78-derived EVs (colored in red). (c) TEM image of HCC78-derived EVs (colored in red) immobilized on the sidewalls of Si nanowires. Scale bar, 100 nm. (d) Immunogold staining by anti-CD63 was employed to verify the identity of EVs captured on Si nanowires. (e) Schematic illustrating the immobilization of 10 nm gold nanoparticles via anti-CD63 onto a tumor-derived EV attached to the sidewall of a Si nanowire by anti-EpCAM. (f,g) Fluorescence microscopy images confirming the capture of HCC78-derived EVs immobilized on the SiNWS using an antibody targeting to the epithelial tumor marker CK. (h) Schematic depicting how anti-EpCAM and anti-CK were used for EV capture and immunostaining of CK, respectively.