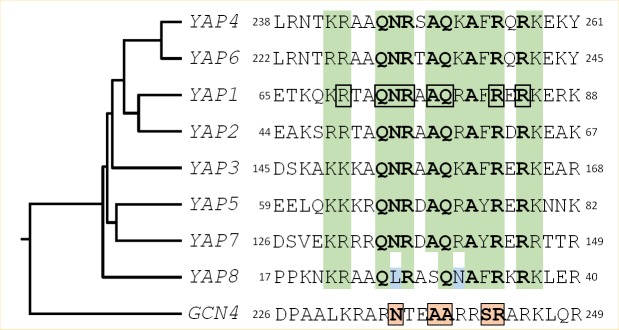
Figure 1. FIGURE 1: Structural features of the Yap family DNA binding domain.
The sequences of the eight Yap DNA binding domains (i.e. the basic region of the bZIP motif) are compared with the equivalent region of Gcn4, the classical yeast AP-1 factor, used as an outgroup. A green background highlights the positions, whose physico-chemical properties are conserved in the Yap family. The most conserved residues are in bold. The Yap8 specific residues are in blue. The Yap1 amino-acids which were predicted to contact DNA based on structural studies [12, 140] have been underlined by a black box. The Gcn4 residues involved in DNA interaction are highlighted by pink boxes. The rooted tree and the multiple alignment were obtained from ClustalW (https://www.genome.jp/tools-bin/clustalw), using the bZIP sequences and the 100 flanking amino-acids.