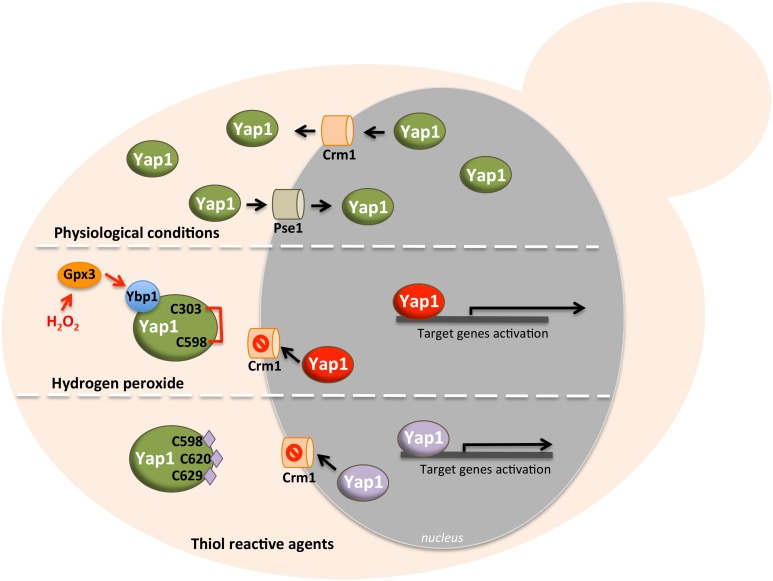
Figure 2. FIGURE 2: Schematic representation of Yap1 activation.
Yap1 has two distinct molecular sensors: one for hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and the other for thiol-reactive compounds (see description in the text). In the first panel is represented the shuttling of Yap1 between the nucleus and cytoplasm, occurring under physiological conditions, entering the nucleus by Pse1 importin and exiting the nucleus by exportin Crm1. In the second panel is depicted the activation of Yap1 by H2O2, which is dependent on Hyr1/Gxp3/Orp1 and Ybp1 proteins. H2O2 induces the formation of a disulfide bond between Cys303 and Cys598 of Yap1, preventing the recognition of the nuclear export signal (NES) by Crm1 (represented in red the activated Yap1). In the third panel is depicted the activation of Yap1 by thiol-reactive agents. These compounds bind to Cys598, Cys620 and Cys629, thereby preventing the recognition of the NES by Crm1 (in purple the activated Yap1). In both cases, the conformational change leads to Yap1 accumulation in the nucleus and posterior gene activation.