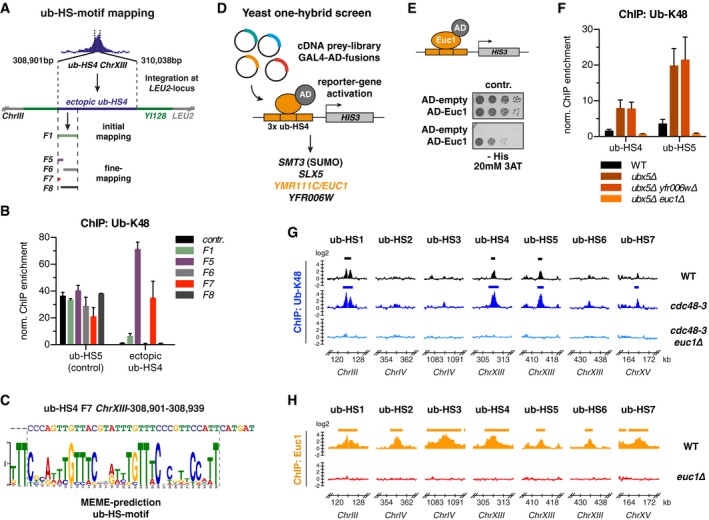
Figure 2. A sequence motif within ub‐hotspots is bound by Ymr111c/Euc1.
-
ASchematic of the ub‐HS‐motif mapping strategy. A 1,038‐bp stretch of ub‐HS4 (blue line) was cloned and integrated at the LEU2 locus (gray) using the integrative YIplac128 vector (green). Initial mapping led to the identification of fragment F1 (Appendix Fig S2A), which was further truncated for fine‐mapping ((B), F5–F8). qPCR primers were designed to bind within the YI128 backbone.
-
BA 39‐bp fragment of ub‐HS4 is sufficient to drive ectopic ub‐HS formation. Fragments of ub‐HS4 were integrated ectopically, and ub‐K48 ChIP‐qPCR was performed for the endogenous ub‐HS5 and the ectopic ub‐HS4 fragments as depicted in (A). contr.: control, empty YIplac128 vector was integrated at LEU2. Experiments were performed in cdc48‐6 background. Data represent means ± SD (n = 2).
-
CExperimental mapping and bioinformatic prediction identify a similar ub‐HS‐motif. Comparison between the experimentally mapped ub‐HS4 F7 (B) and the consensus motif of all ub‐HSs identified by the MEME software.
-
DA yeast one‐hybrid screening strategy to identify proteins binding to the ub‐HS‐motif. Three copies of the ub‐HS4‐motif (F7) were cloned upstream of a minimal promoter followed by a HIS3 reporter gene and integrated at the URA3 locus. A yeast cDNA library with N‐terminally fused Gal4 activation domain (AD) was used to screen for survival on media lacking histidine and multiple plasmids coding for 4 different genes were recovered (bottom). See also Fig EV1G.
-
EEuc1 binds to the ub‐HS‐motif in a Y1H assay. Gal4‐AD‐ or Gal4‐AD‐Euc1‐encoding plasmids were transformed into a Y1H reporter strain as described in (D). Serial dilutions were spotted on control plates and plates lacking histidine with 20 mM 3‐amino‐triazole (3AT). Cells were grown at 30°C for 3 days.
-
FEuc1 is required for the formation of ub‐HSs. ChIP with ub‐K48 specific antibodies was performed for the indicated strains, and enriched DNA was analyzed by qPCR. Data represent means ± SD (n = 4).
-
G, HEuc1 binds to endogenous ub‐HSs. Genome‐wide binding profiles of K48‐linked ubiquitin chains (G) or Euc1 (H) were obtained in ChIP‐chip experiments as described in Fig 1A. Euc1‐ChIP experiments were performed with a polyclonal antibody raised against Euc1 aa 292–462. Data represent means from two independent replicates.
