Figure EV3. Related to Fig 5. Euc181–183 interacts with the Slx5 middle domain (Slx5‐Md, aa 201–335)† .
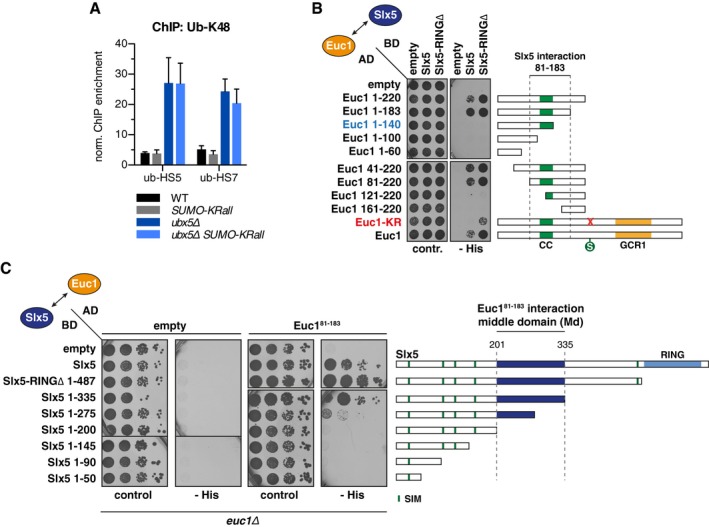
- SUMO‐chain formation is not required for ub‐HS formation. ChIP against ub‐K48 in strains expressing a SUMO variant with all lysines mutated to arginines (SUMO‐KRall) as the only source of SUMO. Enriched DNA was analyzed by qPCR. Data represent means ± SD (n = 3).
- The region of Euc1 required for interaction with Slx5 maps to aa 81–183. Y2H assay to map the Slx5 interaction site on Euc1. Note that SUMOylation‐deficient Euc1‐KR still interacts with Slx5‐RING∆, albeit weaker than wild‐type Euc1 (bottom 2 rows). Cells were grown at 30°C for 2 days.
- The region of Slx5 required to interact with Euc1 maps to aa 201–335. C‐terminal Gal4‐BD‐Slx5 truncation constructs were probed for interaction with Euc181–183 in Y2H. Note that the interaction gradually decreases when truncations between aa 201 and 487 were made. We defined aa 201–335 (middle domain, Slx5‐Md) to be the minimal region required for robust interaction with Euc1 (Fig 5F); however, the region between aa 336 and 487 also contributes to the interaction (compare Slx5‐RING∆ and Slx5‐Md in Fig 5D and G). Cells were grown at 30°C for 3 days.
