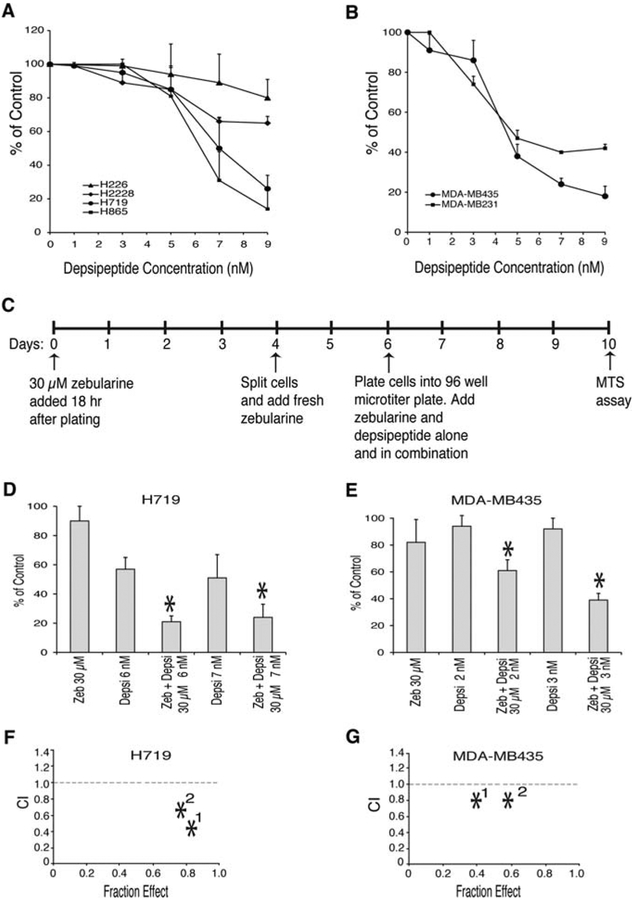
Figure 4.
Enhanced growth inhibition by combined zebularine and depsipeptide treatment in lung and breast cancer cells with hypermethylated CDKN2A. (A) and (B) Effect of depsipeptide on growth of lung and breast cancer cells. (A) Lung cancer (H226, H2228, H865 and H719) and (B) breast cancer (MDAMB231, MDA-MB435) cell lines were treated with the indicated concentrations of depsipeptide as described in Materials and methods. Inhibition of cell growth measured by MTS assay was determined as compared to untreated cells. Data shown represent the mean ± SD of 3–5 experiments. (C) Schematic representation of continuous zebularine and depsipeptide treatment. (D) H719 and (E) MDA-MB435 cells were treated with zebularine (Zeb) alone, depsipeptide (Depsi) alone, or a combination at the concentrations indicated as described in Materials and methods. Inhibition of cell growth is presented as comparison to the untreated controls. (F) CalcuSyn analysis of drug combination in H719 cells showing synergistic drug interaction where no. 1 corresponds to 30 μM zeb and 6 nM depsipeptide and no. 2 corresponds to 30 μM zebularine and 7 nM depsipeptide (G) CalcuSyn analysis of drug combination treatment in MDA-MB435 cells showing additive effect where no. 1 corresponds to 30 μM zebularine and 2 nM depsipeptide and no. 2 corresponds to 30 μM zebularine and 3 nM depsipeptide.