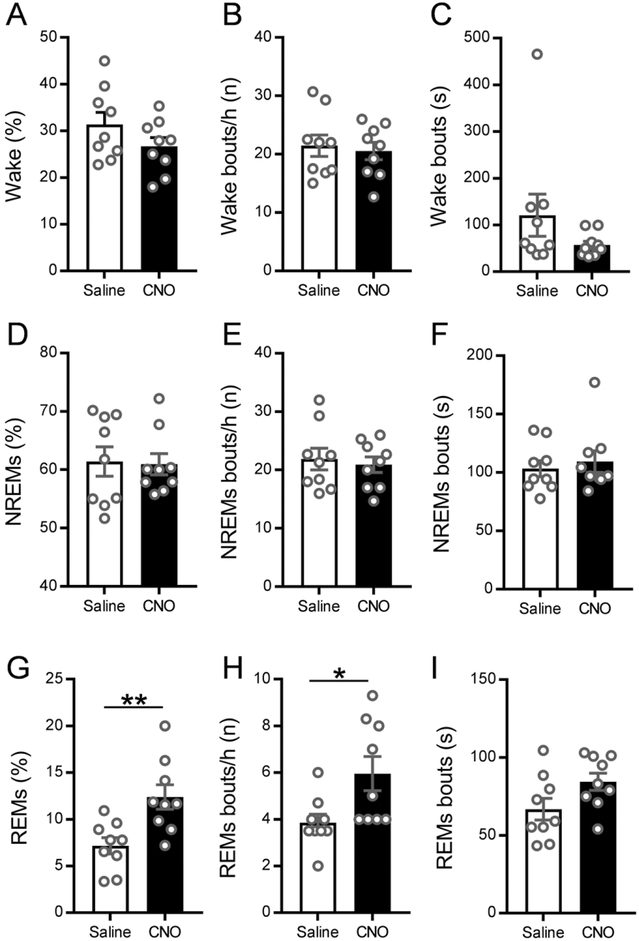
Figure 4: Chemoactivation of MCH neurons specifically increases REMs.
Percentages of time spent in wake, NREMs and REMs (A, D, G), as well as number of bouts (B, E, H) and mean bout duration (C, F, I) during the 3 h recording period after saline (white bars) or CNO (black bars) injections in MCH-Cre mice (n = 9). Saline or CNO (0.3 mg/kg, i.p.) was administered at ZT6 and sleep-wake recordings were conducted between ZT7-ZT10. CNO injections specifically increased the amount of REMs (p=0.0021, 2-tailed paired t-test) and the number of REMs bouts (p=0.0106, 2-tailed paired t-test) without affecting other stages. Data are Mean ± SEM; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01.