Figure 1.
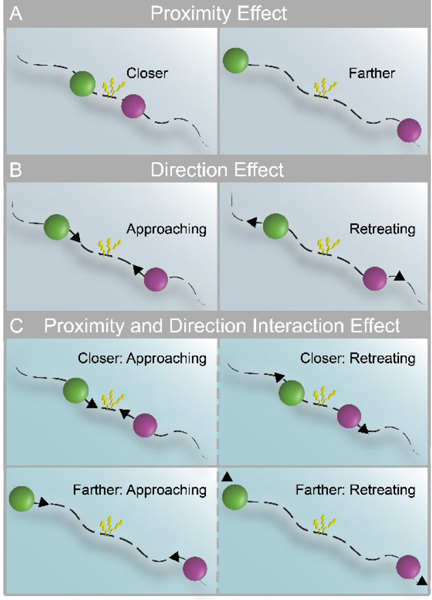
Threat-related factors and their interaction. (A) Closer and farther threat, where threat is represented by an aversive shock when circles touched. (B) Direction of threat: approach vs. retreat. (C) Threat level may depend on both proximity (closer and farther) and direction (left panels indicate approach; right panels indicate retreat).
