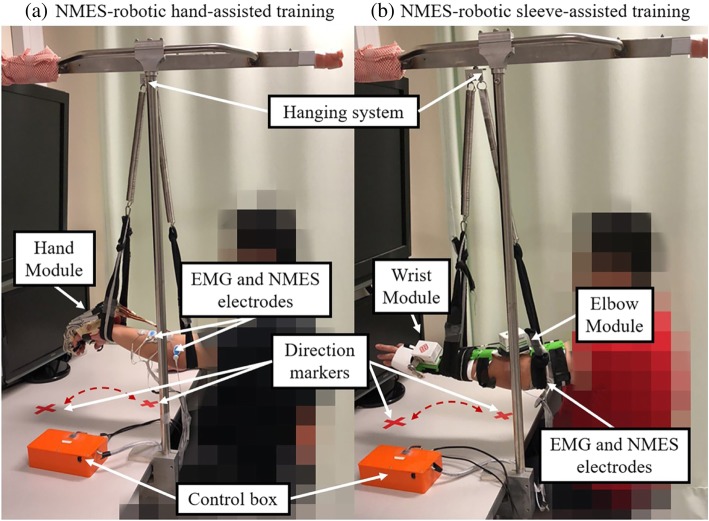
Fig. 1.
The electromyography (EMG)-driven neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES)-robotic system: (a) the NMES-robotic hand consisting of a mechanical exoskeleton of the robotic hand, a pair of NMES electrodes attached to the extensor digitorum (ED) muscle, and EMG electrodes on the ED and the flexor digitorum (FD) muscles; (b) the NMES-robotic sleeve consisting of a mechanical exoskeleton of the wrist module and elbow module, two pairs of NMES electrodes attached to the extensor carpi radialis (ECR) muscle and the triceps brachii (TRI) muscle, and EMG electrodes on the ECR, flexor carpi radialis (FCR), TRI and biceps brachii (BIC) muscles