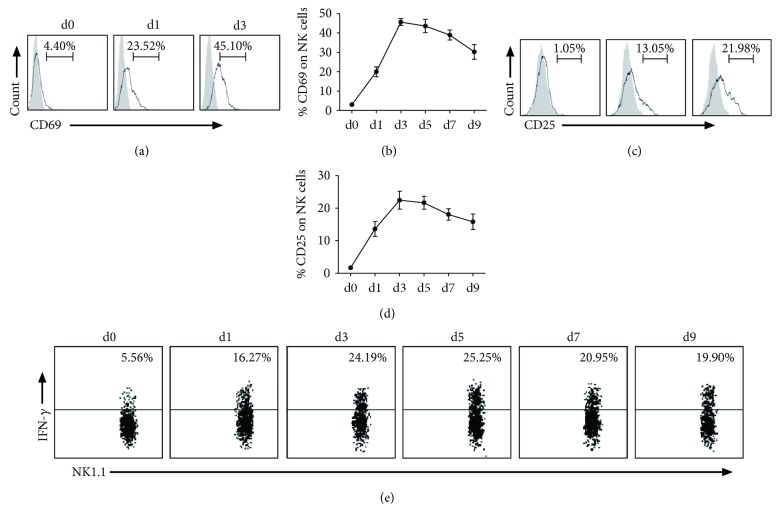
Figure 2.
NK cells become activated and produce IFN-γ in response to Cpn infection. After intranasal infection by Cpn, mice were killed at different days, and splenocytes were stained for NK1.1, CD3e, CD25, and CD69. (a) Representative histogram of activation marker CD69 expression on NK cells at days 0, 1, and 3 p.i.: isotype control Ab staining (gray histograms) and infected mice (solid lines). (b) Kinetics of the expression of CD69 by NK cells. (c) Representative graph of the expression of activation marker CD25 on NK cells after infection: isotype control Ab staining (gray histograms) and infected mice (solid lines). (d) Kinetics of the expression of CD25 by NK cells. (e) Representative staining for intracellular IFN-γ before and after Cpn infection. IFN-γ production by splenic NK cells was assayed by intracellular cytokine staining on gated NK1.1+CD3e- population. The data represent one of at least three independent experiments and are shown as mean ± SD for four mice at end time points.