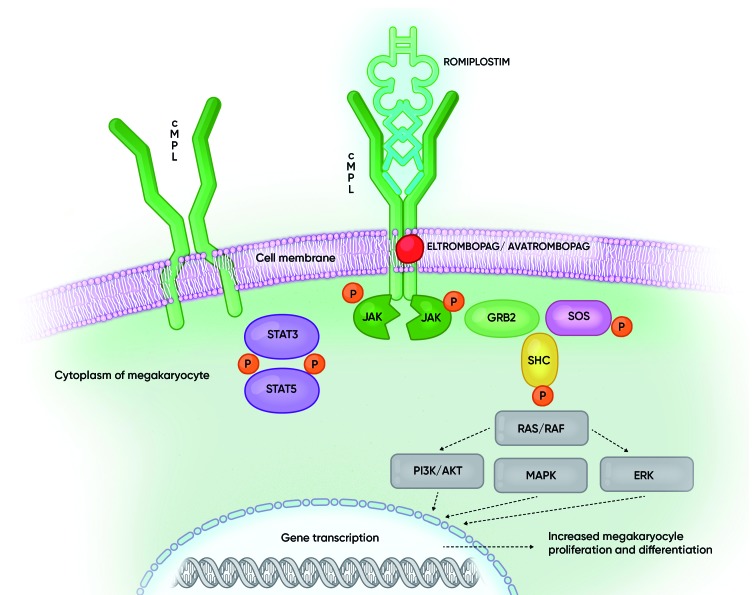
Figure 1.
Cellular mechanisms of action of thrombopoietin (TPO) and of thrombopoietin receptor agonists (TPO-RA). Binding of the ligand (TPO/TPO-RA) to the c-MPL receptor on the megakaryocyte causes conformational change in the receptor, resulting in downstream activation of the various signaling pathways including JAK2/STAT5, PI3K/AKT, ERK, ultimately resulting in increased platelet production. Various pathways can be activated by the different substances (see also Table 1). GRB2: growth factor receptor-binding protein 2; JAK: Janus kinase; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; P: phosphorylation; RAF: rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma kinase; RAS: rat sarcoma GTPase; SHC: Src homology collagen protein; STAT: signal transducer and activator of transcription; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases; ERK: extracellular-signal-regulated kinase.