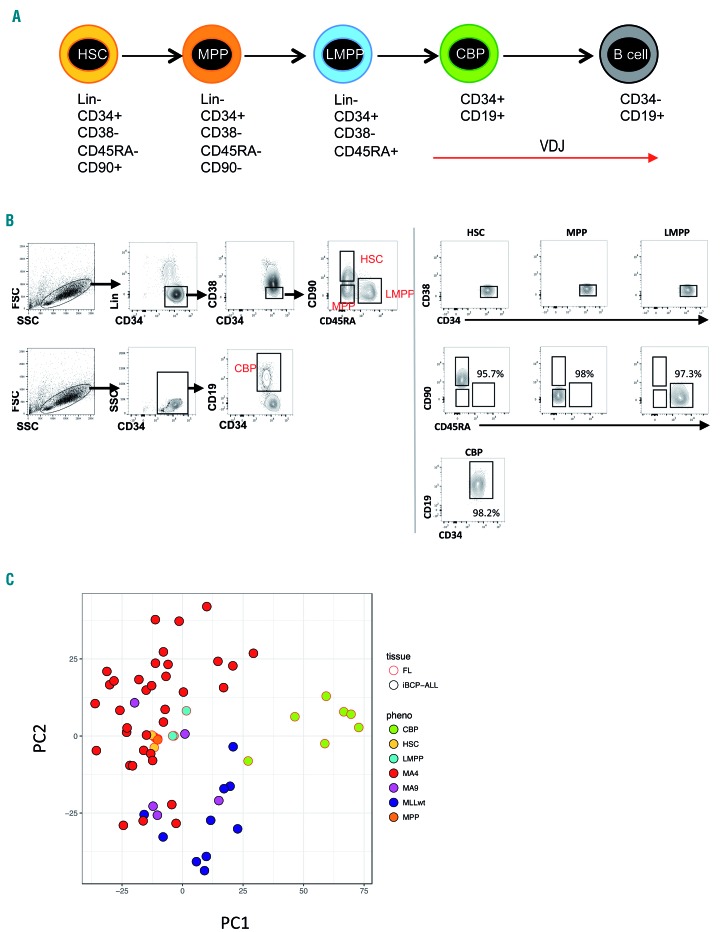
Figure 7.
Comparison of the transcriptome of human fetal CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell populations to infant B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. (A) Schematic representation of B-cell development in human fetal liver (FL) showing immunophenotypic definitions for hematopoietic stem cells (HSC), multipotent progenitors (MPP), lymphoid-primed multipotent progenitors (LMPP), committed B progenitors (CBP) and B cells. The onset and expected patterns of IgH rearrangements59,60 are depicted as red arrows. (B) Sorting strategy for FL hematopoietic stem and progenitor (HSPC) populations by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. The sorting gates for each population are shown in representative flow plots on the left. The purity of the sorted populations is depicted on the right demonstrating >95% purity. (Lin, Lineage cocktail). (C) Principal component analysis of gene expression of infant B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (iBCP-ALL) samples (n=42) and FL HSPC populations (n=3-7) using the top 1,000 variably expressed genes, as determined by RNA-sequencing. FL HSPC as in (A); MAF4, MLL-AF4+ iBCP-ALL; MA9, MLL-AF9+ iBCP-ALL; MLLwt, MLL wildtype iBCP-ALL.