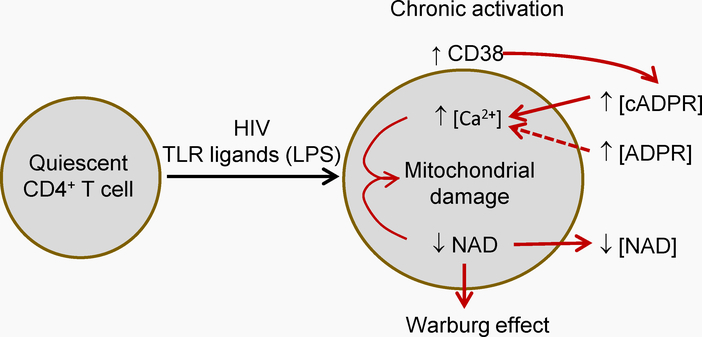
Figure 1.-. General hypothesis outline.
HIV infection is accompanied by chronic activation of CD4 T cells and CD8 T cells (among others). This increases CD38 catalytic activity in the milieu of CD4 T cells. CD38 activity removes cytoplasmic NAD from CD4 T cells and yields the calcium-mobilizing compounds cyclic adenosine diphosphate ribose (cADPR) and adenosine diphosphate ribose (ADPR). cADPR and ADPR increase cytoplasmic Ca2+. Together, these effects reduce mitochondrial function and integrity, leading to a decreased cell viability in the long term. Dotted line indicates that less evidence is available.