Graphical Abstract.
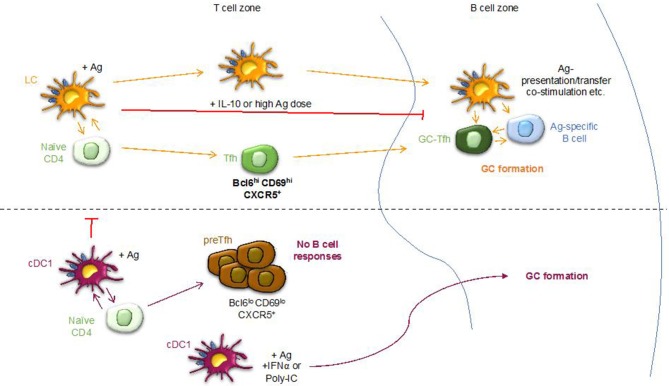
Sequential activation model. LCs and cDC1s regulate humoral immune responses by supporting the differentiation of distinct Tfh cells. LCs, unlike cDC1s support GC-dependent antibody responses in the absence of an adjuvant. LCs first induce the formation of Tfh cells and then, likely licensed by the Tfh cells, migrate to the B cell area to initiate B cell responses. The GC responses induced by LCs were inhibited by: targeted delivery of IL-10, high antigen dose and co-delivery of antigen to cDC1s. cDC1s were able to support GC-dependent humoral immune responses in inflammatory settings, in the presence of poly-IC or targeted delivery of IFNα.