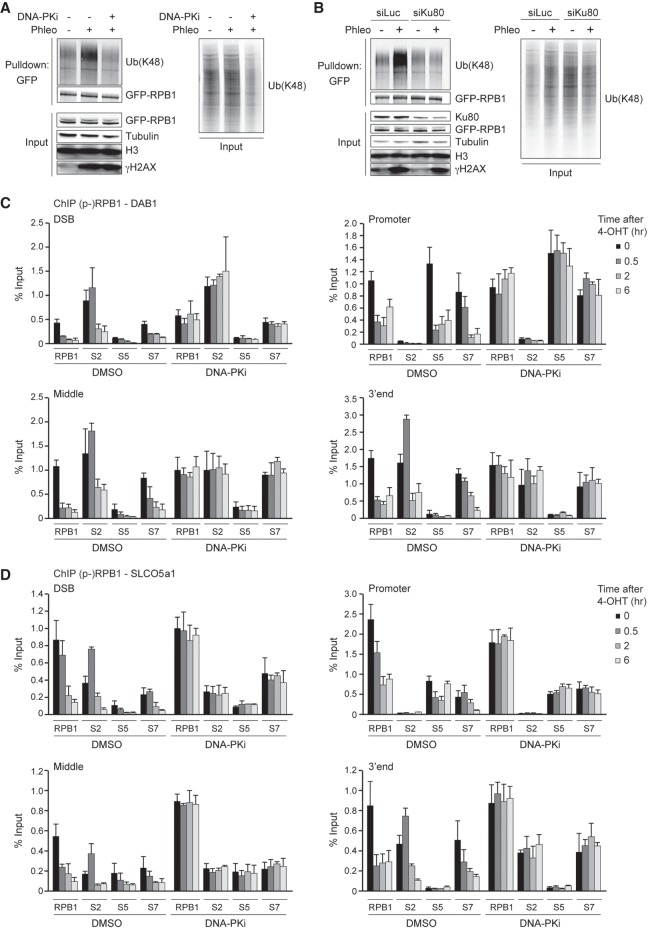
Figure 4.
DNA-PK affects the ubiquitylation and occupancy of RPB1. (A) Pull-downs of GFP-RPB1 under denaturing conditions in phleomycin (Phleo)- and DNA-PK inhibitor (DNA-PKi)-treated U2OS cells. Cells were also treated with proteasome inhibitor (MG-132) 25 min before the phleomycin treatment. Blots were probed for Ub(K48), GFP, H3, and γH2AX. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) As in A, except that cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA. (C) ChIP-qPCR against RPB1 and S2-, S5-, or S7-phosphorylated RPB1 (p-RPB1) in DMSO-treated (control) and DNA-PKi-treated U2OS HA-ER-I-PpoI cells at the indicated time points after 4-OHT treatment and at the indicated positions at DAB1. A representative experiment is shown. A repeat of the experiment is shown in Supplemental Figures S10A and S11A. (D) ChIP-qPCR against RPB1 and S2-, S5-, or S7-phosphorylated RPB1 (p-RPB1) in DMSO-treated (control) and DNA-PKi-treated U2OS HA-ER-I-PpoI cells at the indicated time points after 4-OHT treatment and at the indicated positions at SLCO5a1. A representative experiment is shown. A repeat of the experiment is shown in Supplemental Figures S10B and S11B.