Fig. 2.
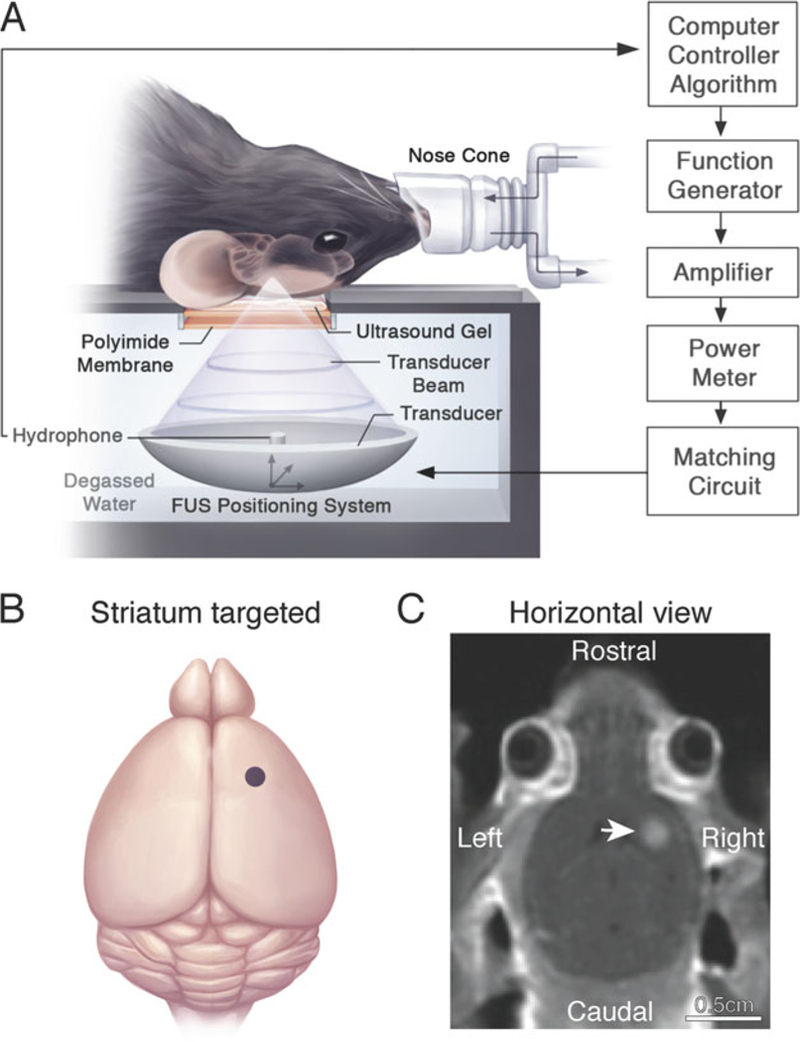
MRIgFUS-mediated BBB permeability in the unilateral mouse striatum. (a) The animal is placed in the supine position on an MRI-compatible sled. The skull is coupled to a polyimide membrane with ultrasound gel. A second polyimide membrane is coupled to a degassed, deionized water tank containing the transducer and hydrophone positioned in the center of the transducer. Sonication parameters and procedures are described in Subheading 3.3. (b) Relative neuroanatomical location of the FUS focal spot targeted to the striatum (indicated by a purple dot). Target locations in the brain are selected on axial T2-weighted MR images. (c) Post-sonication, a contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR image is used to visualize the entry of an MRI contrast agent, Gadovist, in the sonicated mouse striatum (indicated by a white arrow) and confirm BBB opening in the targeted location. Increased voxel intensity in the sonicated region is proportional to the extent of BBB permeability and amount of virus delivered into the brain. Reproduced with permission from Sunnybrook Research Institute
