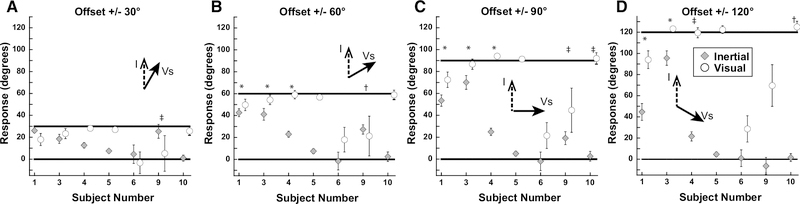
Figure 6.
Results of experiment 2 by subject. The values represent the average of all inertial stimulus offsets. These results represent a variation in perception by subject: subjects #3, 4, and 10 tended to perceive the visual and inertial stimuli in different directions while the remaining subjects reported them in a similar direction. Error bars represent ±1 SEM. *: significant shift in heading perception vs 0° offset in both positive and negative offsets (i.e. ±30°). †: significant shift in heading perception vs 0° offset in positive offset (i.e. +30°), but not negative offset (i.e. −30°). ‡: significant shift in heading perception vs 0° offset in negative offset (i.e. −30°), but not negative offset (i.e. +30°). Significance measured using rmANOVA; Bonferroni test.