Fig 1. HRCT patterns and histology findings.
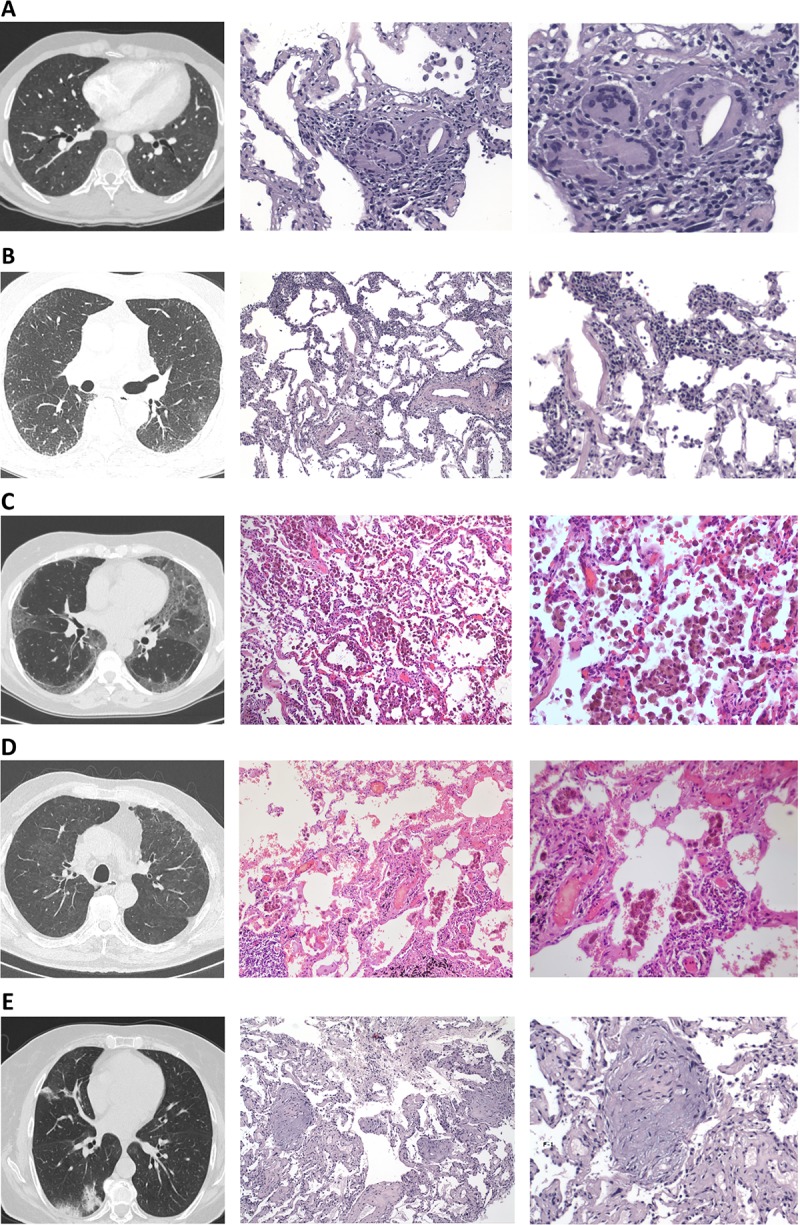
(A) Patient 1: HRCT (pulmonary window) demonstrating diffuse ground glass opacities, small ill-defined centrilobular nodules, lobular areas of decreased attenuation (mosaic pattern) with a histological pattern consistent with hypersensitivity pneumonitis demonstrating poorly formed non-necrotizing granulomas (x20 and 40 respectively) and a definite diagnosis after MDT review of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. (B) Patient 2: HRCT (pulmonary window) demonstrating areas of ground glass opacities mainly involving the left lower lobe and mild peripheral reticulation with a histological pattern of cellular non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) with diffuse, evenly distributed, moderate chronic inflammation, without effacement of the alveolar architecture or evident granulomas a patient diagnosed with (x10 and 20 respectively) and a definite diagnosis after MDT review of undifferentiated form of CT-ILD. (C) Patient 3: HRCT (pulmonary window) demonstrating bilateral areas of ground glass opacities with peripheral and subpleural predominance with a histological pattern compatible with desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP-like reaction) with intraalveolar macrophage aggregates and alveolar septae with mild focal interstitial fibrosis (x10 and 20 respectively) and a definite diagnosis after MDT review of smoking related interstitial lung disease (SR-ILD). (D) Patient 4: HRCT (pulmonary window) demonstrating bilateral patchy areas of ground glass opacity, mild subpleural intralobular linear opacities with a histological pattern of respiratory bronchiolitis (RB) with the presence of histiocytes in a centroacinar rather than in a diffuse pattern (x10 and 20 respectively) and a definite diagnosis after MDT review of smoking related interstitial lung disease (SR-ILD). (E) Patient 5: HRCT (pulmonary window) demonstrating sub-pleural and peribronchial consolidation in the posterior segment of right lower lobe and middle lobe with a histological pattern of organizing pneumonia (OP) showing the presence of exudate of inflammatory cells, foam cells, fibroblastic Masson bodies and macrophages creating a bronchiolar obstruction (x10 and 20 respectively) and a definite diagnosis after MDT review of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP).
