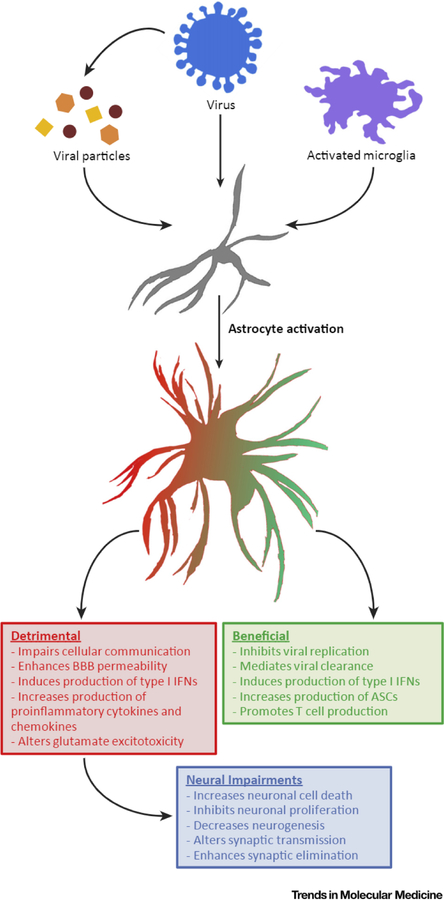
Figure 1. The Duality of Reactive Astrocytes during and after Viral Infection.
Astrocytes transition into an activated state through multiple mechanisms, such as direct viral infection or indirectly via viral particles and/or activated microglia. Reactive astrocytes can exhibit both beneficial (green box) and detrimental (red box) roles during viral infection and recovery from viral infection. Damaging roles of activated astrocytes have been linked to immunopathology that may lead to more long-term neurological disease symptoms (blue box) after recovery from viral infection. Abbreviations: ASC, Antibody-secreting cells; BBB, blood-brain barrier; CNS, central nervous system; INF, interferon.