Figure 1.
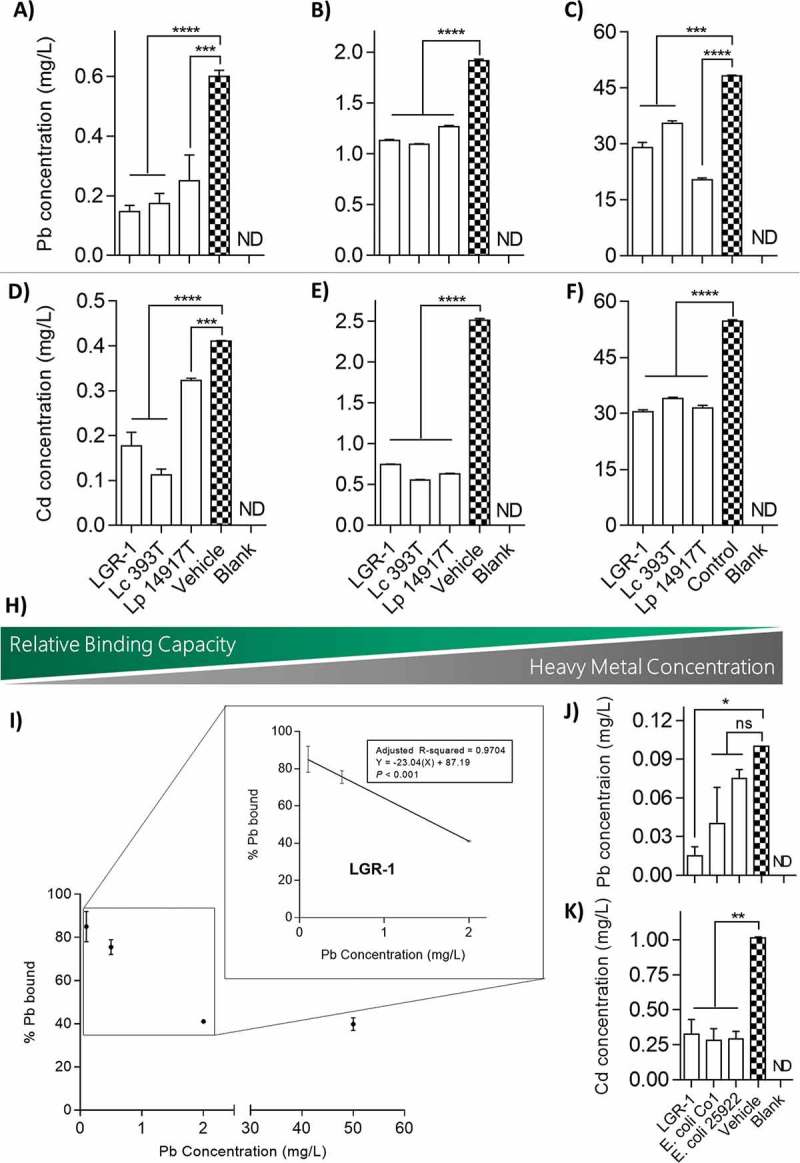
In vitro sequestration of Pb and Cd by lactobacilli. Overnight cultures of lactobacilli were re-suspended in 50 mM HEPES buffer with Pb at concentrations of (A) 0.5 mg/L, (B) 2.0 mg/L, and (C) 50 mg/L, or alternatively with Cd at concentrations of (D) 0.5 mg/L, (E) 2.5 mg/L, and (F) 50 mg/L. (H) Visual representation of the inverse relationship between relative binding capacity of lactobacilli and concentration of Pb and Cd in solution. (I) Linear regression analysis of relative binding potential of LGR-1 compared to amount of Pb in solution. Binding potential of (J) Pb at a concentration of 0.1 mg/L and (K) Cd at a concentration of 1.0 mg/L was compared between LGR-1 and two strains of lab-strain E. coli. All experiments were performed from 3 independent experiment and analyzed in triplicate. Pb and Cd were quantified using an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrophotometer. Error bars represent ± standard error. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001. ND = not detected. ns = not significant.
