Figure 2.
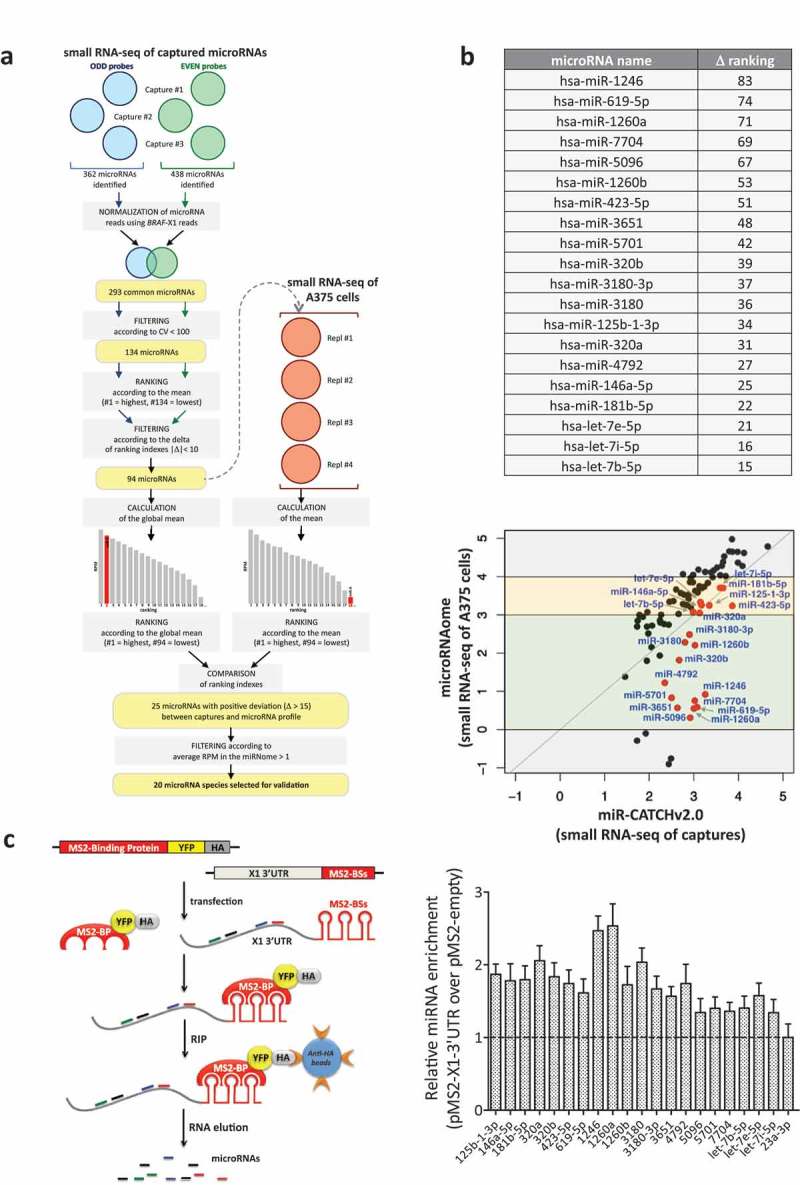
Identification of X1-binding microRNAs from small RNA-seq data.
(a). Description of the analytical steps followed in order to select the microRNAs to be validated (see text for details).
(b). (upper) List of the 20 selected microRNAs, ordered by difference in ranking index between the small RNA-seq of A375 cells and the small RNA-seq of captured microRNAs (see column N in Supplementary Table S3). (lower) Expression levels (log10(RPM mean)) of the 94 microRNAs in the small RNA-seq of the captures (X axis) and of A375 cells (Y axis). As indicated by the red dots, which represent the 20 selected microRNAs, overall our analytical approach prioritizes for experimental analysis the microRNA species that have intermediate expression levels in A375 cells (yellow and green middle boxes), while it discards those that are expressed at very high or very low levels (top and bottom grey boxes, respectively).
(c). (left) Cartoon describing the MS2-tagged RNA affinity purification (MS2-TRAP) assay (modified from [24]). This assay is based on the use of two plasmids. The pMS2-X1-3ʹUTR plasmid (right) expresses 12 copies of the MS2 binding site (BS), which is characterized by a defined secondary structure; furthermore, the presence of a multiple cloning site upstream of the MS2-BSs allows the insertion and co-expression of BRAF-X1 3ʹUTR. The other plasmid is called pMS2-BP (left) and expresses the MS2-Binding Protein (MS2-BP) fused with YFP and the HA-Tag. The MS2-BP, which is able to bind to MS2-BS, can be efficiently immunoprecipitated using the anti-HA antibody. Upon the co-transfection of the two plasmids inside the cells, a ribonucleoproteic complex is formed between the MS2-BP-YFP-HA chimerical protein and the BRAF-X1 3ʹUTR/MS2-BSs, to which endogenous microRNAs are physically bound. Such complex can be immunoprecipitated using anti-HA sepharose beads, so that, upon RNA extraction, the bound microRNAs can be quantified by qRT-PCR. (right) The qRT-PCR detection of the microRNAs identified by miR-CATCHv2.0 was performed on BRAF-X1 3ʹUTR immunoprecipitated using the MS2-TRAP assay. miR-23a-3p, which is depleted in the captures compared to the microRNA profile of A375 cells, is taken as negative control. The graphs in this figure represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.
