Figure 3.
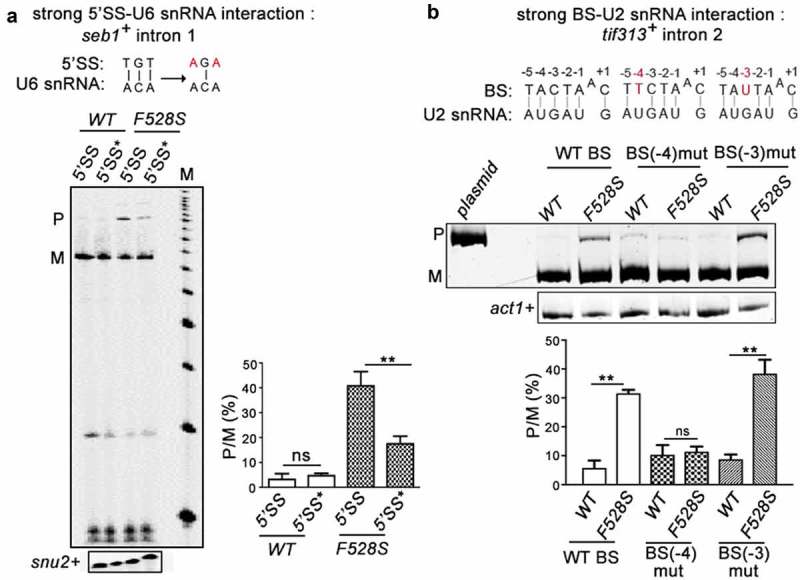
SpPrp16 destabilizes 5’SS-U6 snRNA and BS-U2 snRNA interactions. (a) Primer extension to assess the splicing of seb1+ E1-I1-E2 mini-transcripts having wild-type or mutant 5’SS (depicted as 5’SS and 5’SS* respectively) in the WT (leu1:spprp16+) and F528S (leu1:spprp16F528S) mutant cells. The mutations introduced in the 5’SS (highlighted in red) and positions which can base-pair with U6 snRNA are shown (black lines). Primer extension on snu2+ transcripts served as the loading control. Lane M- 100 nts to 1000 nts DNA size marker (b). Semi-quantitative RT-PCRs to analyse the splicing of tif313+ intron2 in mini-transcripts comprising exon2-intron2-exon3 with wild-type or mutant branch site (BS) in the WT (leu1:spprp16+) and F528S (leu1:spprp16F528S) mutant strains. The mutations introduced (highlighted in red) and the positions that can base-pair with U2 snRNA are shown (black lines).
