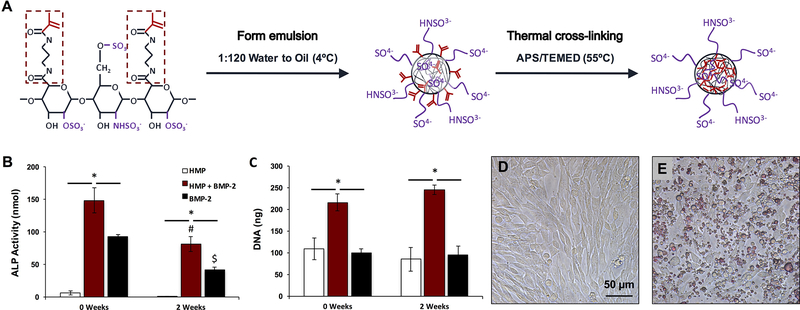
Figure 1.
Heparin microparticle fabrication and in vitro characterization. A) Schematic of HMP fabrication process. Heparin methacrylamide was dissolved in water and emulsified in oil. The emulsion was heated to promote free radial cross-linking of the methacrylamide groups. B) HMP-bound BMP-2 bioactivity was evaluated by culturing C2C12 cells for 72 h with soluble BMP-2 and BMP-2-loaded HMPs, and evaluating ALP activity and DNA content. BMP-2-loaded HMPs induced higher total ALP activity than unloaded HMPs or soluble BMP-2, but ALP activity induced by both BMP-2-containing groups decreased after 2 weeks of pre-incubation at 37 ºC. (* = p < 0.05 as indicated; # = p < 0.05 compared to loaded MPs (0 weeks); $ = p < 0.05 compared to soluble BMP-2 (0 weeks)) C) BMP-2-loaded HMPs yielded greater DNA content after 3 days compared to unloaded HMPs and soluble BMP-2 treatment at both 0 and 2 weeks. (* = p < 0.05 as indicated) D) Representative images of C2C12 cells cultured for 72 h alone or E) with 0.1 mg of HMPs stained with DMMB for contrast.