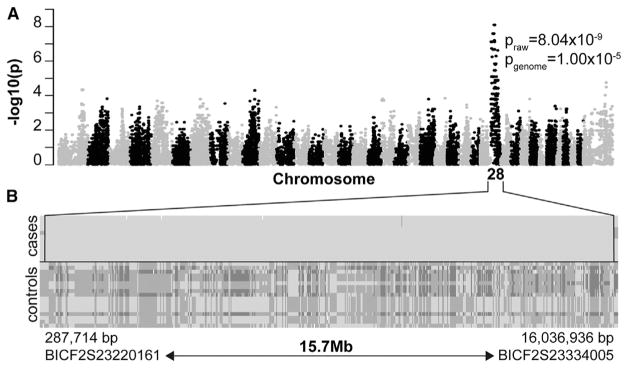
Figure 2. Mapping the ISCWT Microphthalmia Locus.
(A) Summary of GWAS data. Manhattan plot of a genome-wide case-control association analysis, with 12 cases and 17 controls, shows localization of microphthalmia trait on CFA28, with a corrected probability value Pgenome = 1.00 × 10−5.
(B) Genotype data showing a shared haplotype block in microphthalmic dogs (cases). Each row represents a single animal, with the genotypes at each SNP locus (columns) indicated by dark (AA), intermediate (AB), or light (BB) shading, in relation to the affected haplotype (BB). Every affected dog is homozygous within this segment. The 15.7-Mb critical region spans approximately 38% of CFA28, near the centromere, and it is delimited by SNP markers BICF2S23220161 (centromeric) and BICF2S23334005 (telomeric).
See also Figure S1.