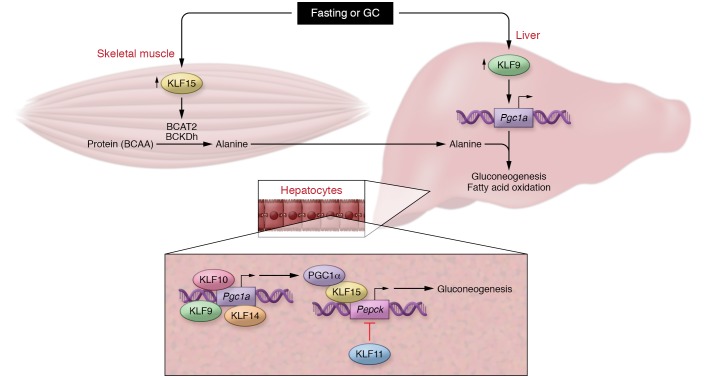
Figure 1. KLF9 participates in a KLF metabolic network.
Upper panel: Proposed model by which fasting or GC release concurrently increases expression of skeletal muscle KLF15 and hepatic KLF9 to coordinate gluconeogenesis. KLF15 facilitates BCAA catabolism to provide carbon substrates (alanine) for gluconeogenesis via induction of BCAT2 and BCKDh, while KLF9 increases transcription of the gluconeogenic coactivator Pgc1a. Lower panel: Redundancy in hepatic KLF function preserves glycemic control during fasting. KLF9, KLF10, and KLF14 increase transcription of Pgc1a, while KLF15 serves as a cofactor to increase transcription of the rate-limiting enzyme Pepck. Conversely, KLF11 represses Pepck transcription, thereby inhibiting gluconeogenesis in fed states.