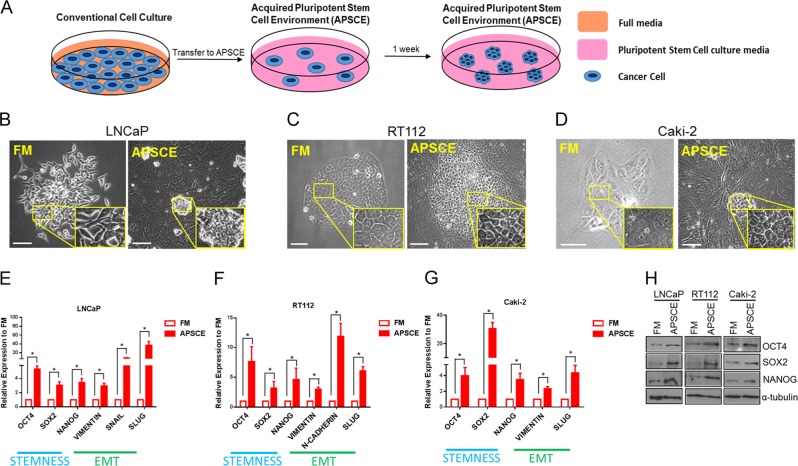
Fig. 2.
A preclinical model to recreate a stem cell-like aggressive cancer phenotype. a Schematic of culture details of generation of Acquired Pluripotent Stem Cell Environment (APSCE). Briefly, cancer cells were transferred from culture in their regular serum supplemented medium (FM) to culture conditions used for human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) as described in ‘Materials and methods’. Following culture of cancer cells in APSCE, tight colonies consisting of smaller cells, morphologically similar to that of ESCs and iPSCs, were observed. b–d Prostate (LNCaP), bladder (RT112) and renal (Caki-2) cancer cell growth in serum supplemented medium (FM) and APSCE after 7 days. Of note, for cells cultured in APSCE, feeder cells were used though no MACS selection was performed. e–g Stemness (OCT4, SOX2, NANOG) and mesenchymal (vimentin, Snail, Slug, N-cadherin) gene expression was measured by quantitative PCR (qPCR) following culture in FM vs APSCE in LNCaP, RT112 and Caki-2 cells. Data represents at least three independent experiments ± SEM (*denotes p-value < 0.05). Of note, EMT characterisation studies were carried out without feeders in APSCE to avoid any mesenchymal cell contamination. h Western blot analysis demonstrating OCT4, SOX2 and NANOG protein expression following culture in FM and APSCE in LNCaP, RT112 and Caki-2 cells, using α-tubulin as loading control