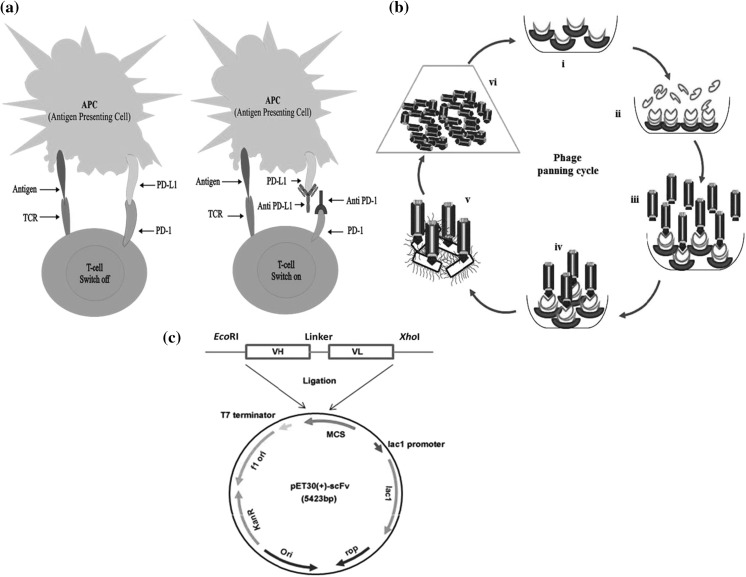
Fig. 1.
a Inhibition of PD-L1/PD-1 immune checkpoints with antibodies. Binding of PD-L1 and PD-1 inhibits proliferation and activation of T cell result cell exhaustion. This phenomenon can be reversed by blocking PD-L1/PD-1 binding with monoclonal antibodies. b Phage display bio-panning cycle. Phage bio-panning cycles: (i) immobilization of Ni–NTA sefinose beads on the solid surface. (ii) Binding of PD-L1 antigen with beads. (iii) Incubation of phage library. (iv) Removal of unbound phages via washing and selective phages are eluted out. (v). Infection of E. coli by rescued positive phages. (vi) Positive phage enrichment. c Genetic map of recombinant vector pET30 (+) scFv construction. The vector contains a Lac operon promoter region, gene encoding kanamycin resistance gene, the origin of replication fused with desired anti-PD-L1 scFv sequences including VH, VL and linker sequences loaded with EcoRI and XhoI restriction sites