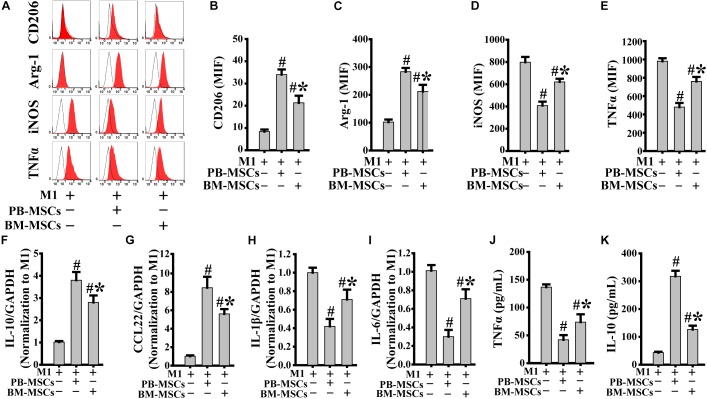
FIGURE 3.
PB-MSCs triggered M1-type polarization toward M2 type. (A–E) PB-MSCs more effectively increased the expression of CD206 and Arg-1 in LPS-induced M1-type macrophages co-cultured with BM-MSCs using the Transwell system for 3 days, as determined by flow cytometry for M1 (i.e., iNOS and TNFα) or M2 (i.e., CD206 and Arg-1) typical markers. (F–I) The expression of pro-inflammatory (e.g., IL-6 and IL-1β) and anti-inflammatory (e.g., IL-10 and CCL-22) factors was determined using a real-time PCR in M1 macrophages co-cultured with either PB-MSCs or BM-MSCs for 3 days. (J,K) The levels of pro-inflammatory cytokine (e.g., TNFα) and anti-inflammatory cytokine (e.g., IL-10) factors were determined by using ELISA in supernatants of M1-type macrophages co-cultured with either PB-MSCs or BM-MSCs for 3 days. n = 5, #p < 0.05, vs. M1 co-cultured without either PB-MSCs or BM-MSCs, ∗p < 0.01, vs. M1 co-cultured with either PB-MSCs.