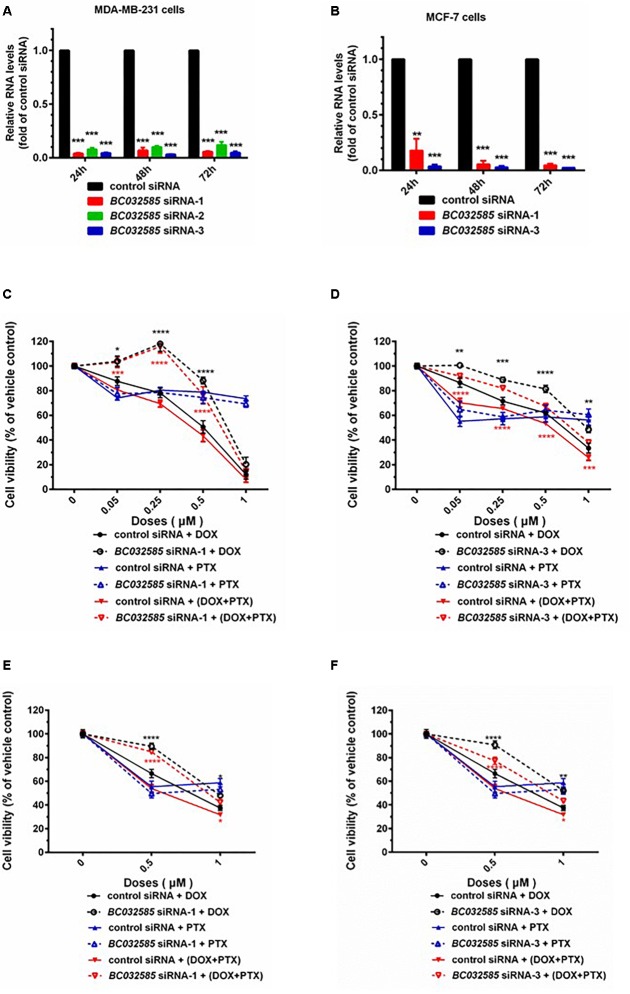
FIGURE 5.
Knockdown of BC032585 lncRNA increases cell resistance to chemotherapeutic agents in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. (A,B) MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells were transfected with a specific BC032585 siRNA (BC032585 siRNA –1, 2, 3, and 100 nM), or a negative control siRNA (control siRNA) for 24, 48, and 72 h. The transfected cells were then harvested for quantification of BC032585 lncRNA by real-time PCR. The RNA levels were expressed as fold of corresponding controls, and the data are mean ± SD of three independent experiment. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared to the corresponding controls. (C,D) MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with either BC032585 siRNAs or control siRNA for 24 h, and then plated in 96-well plates and treated with various doses of DOX alone or in combination with 0.05 μM PTX for 48 h. The number of viable cells (cell viability) was determined at the end of treatment and expressed as a percentage of corresponding vehicle control. The data are the mean ± SEM of two or three independent triplicate experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared to corresponding controls. (E,F) MCF-7 cells in 96-well plate were transfected with either BC032585 siRNAs or control siRNA for 48 h and then treated with various doses of DOX alone or in combination with 0.05 μM PTX for another 48 h. The number of viable cells (cell viability) was determined at the end of treatment and expressed as a percentage of corresponding vehicle control. The data are the mean ± SEM of two or three independent triplicate experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 compared to corresponding controls.