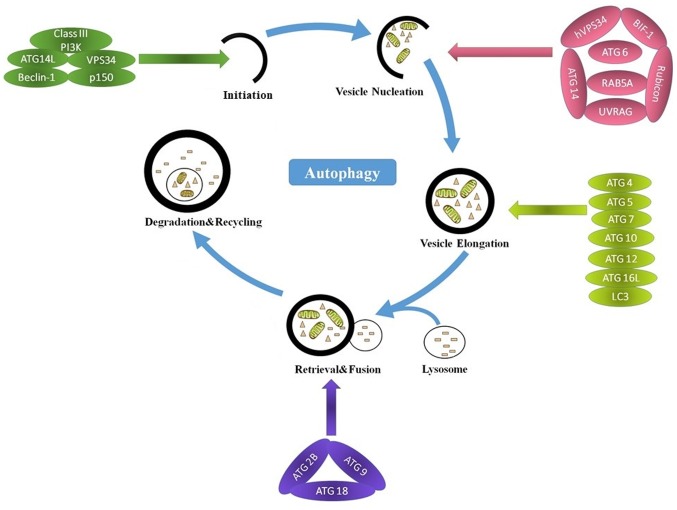
Figure 2.
Main steps in autophagy and the molecular regulators involved. Autophagy occurs sequentially in five main steps: Initiation, vesicle nucleation, autophagosome elongation, retrieval and degradation. During the initiation, the formation of a Beclin 1, class III PI3K, VPS34, ATG14L and p150 complex contributes to the initiation and progression of autophagy. Vesicle nucleation is mediated by hVPS34, BIF-1, ATG6, ATG14, Rubicon, RAB5A and UVRAG. Autophagosome elongation is mediated by the ATG16L complex (ATG4, ATG5, ATG7, ATG10, ATG12 and ATG16L) and LC3. Retrieval is mediated by ATG2B, ATG9 and ATG18. In the last stage, engulfed contents are degraded following the fusion of the autophagosome with a lysosome, and the nutrients and energy are recycled. PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; VPS34, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit type 3; ATG, autophagy related; LC3, microtubule associated protein 1 light chain 3 α; RAB5A, RAB5A, member RAS oncogene family; BIF1, zinc finger and BTB domain containing 24; UVRAG, UV radiation resistance associated.