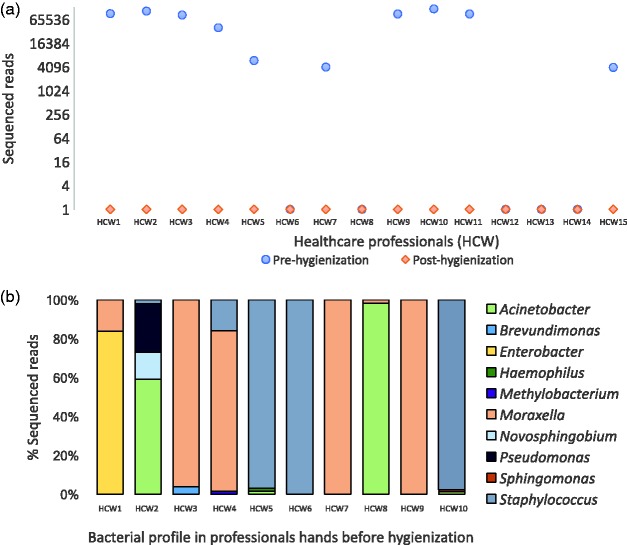
Figure 2.
Tracking hygienization of the hands of healthcare professionals. DNA sequencing was performed directly from swab samples collected from healthcare workers (HCW1 to HCW15) before and after hand hygienization. (a) Pre-hygienization samples have larger numbers of reads for the bacterial 16S rRNA gene. After the hands cleaning protocol, the total number of reads sharply decreases, showing an effective hygienization process. Additionally, one advantage of using high-throughput DNA sequencing is to assess the microbial diversity present in samples and know which microorganisms are present. (b) Identification of bacterial genera sequenced from healthcare professional hands. Generally, species involved in healthcare-associated infections (HAI) and potential pathogens were found (e.g. Staphylococcus, Acinetobacter, Enterobacter, Pseudomonas), highlighting the importance of large-scale monitoring of processes to improve healthcare assistance and decrease HAI. (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.)