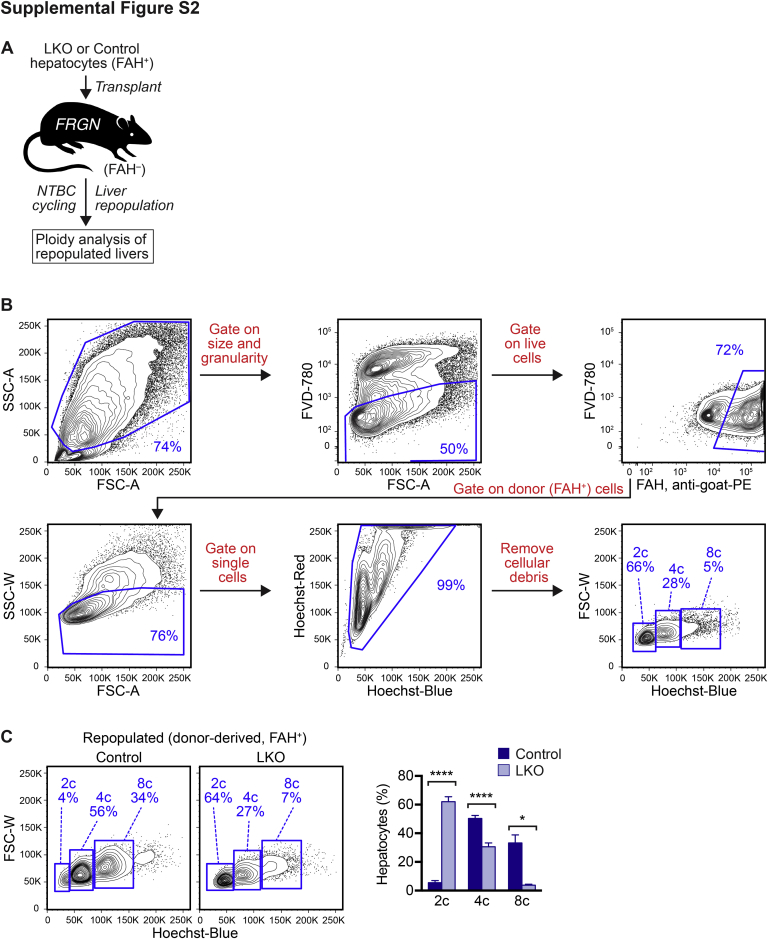
Supplemental Figure S2.
Hepatocytes from E2f7/E2f8-deficient livers remained predominantly diploid during extensive in vivo proliferation. A: Approximately 300,000 hepatocytes from control and liver-specific E2f7/E2f8 double knockout (LKO) mice (males, 4 months old) were transplanted into FRGN (Fah–/–Rag2–/– IL-2 common γ chain–/– Nod background) recipient mice (females, 2 months old) and subjected to 2-(2-nitro-4-trifluoro-methylbenzoyl)-1,3-cyclo-hexanedione (NTBC) cycling to promote liver repopulation by transplanted donor cells. After completed repopulation, livers that contained a mixture of fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase positive (FAH+) donor hepatocytes and FAH– host hepatocytes were isolated and stained with Fixable Viability Dye (FVD)–780, Hoechst, and FAH antibody (donor marker). B: Cells were first gated on the basis of size/granularity and viability. Single cells were then selected and cellular debris was removed. Donor-derived cells (FAH+) were selected and hepatic ploidy populations was determined. Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) plots are shown for an FRGN mouse repopulated by LKO hepatocytes. C: The distribution of hepatic ploidy populations of live FAH+ donor-derived hepatocytes from mice repopulated with control or LKO hepatocytes are shown in representative flow cytometric plots and summarized in the graph. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (C). n = 4 mice repopulated with control hepatocytes (C); n = 4 mice repopulated with LKO hepatocytes (C). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001. 2c, diploid hepatocytes; 4c, tetraploid hepatocytes; 8c, octaploid hepatocytes; FSC-A, forward scatter area; FSC-W, forward scatter width; SSC-A, side scatter area; SSC-W, side scatter width.