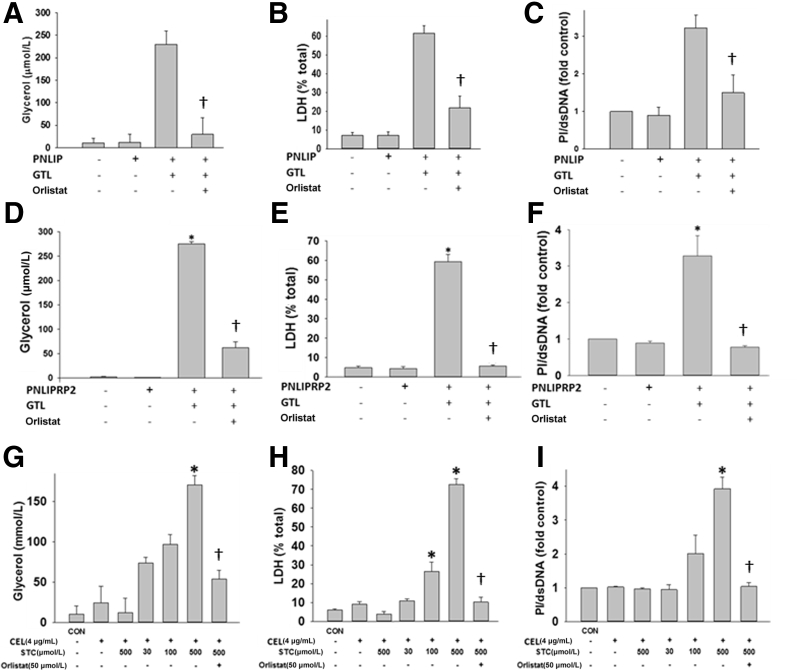
Figure 5.
Bar graphs comparing human pancreatic triacylglycerol lipase (hPNLIP; 1 μg/mL), human pancreatic lipase-related protein 2 (hPNLIPRP2; 1 μg/mL), and human carboxyl ester lipase (hCEL; 4 μg/mL) on lipotoxic parotid acinar necrosis. Parotid acini were exposed to exogenous glyceryl trilinoleate (GTL; 300 μmol/L) in the presence of recombinant lipases. In case of hPNLIP and hPNLIPRP2, no bile acids were present in the medium. The concentration of sodium taurocholate (STC) used for CEL is shown under the corresponding bars. The experiments were performed for 4 hours. Lipolysis was measured by glycerol release (A, D, and G), and cell injury in terms of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) leakage (B, E, and H) and propidium iodide (PI) uptake (C, F, and I) were measured with or without the lipase inhibitor orlistat (50 μmol/L). Note CEL required ≥100 μmol/L STC to induce cell injury. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = at least 3 independent experiments. ∗P < 0.05 versus control (CON); †P < 0.05 versus without orlistat. dsDNA, double-stranded DNA.