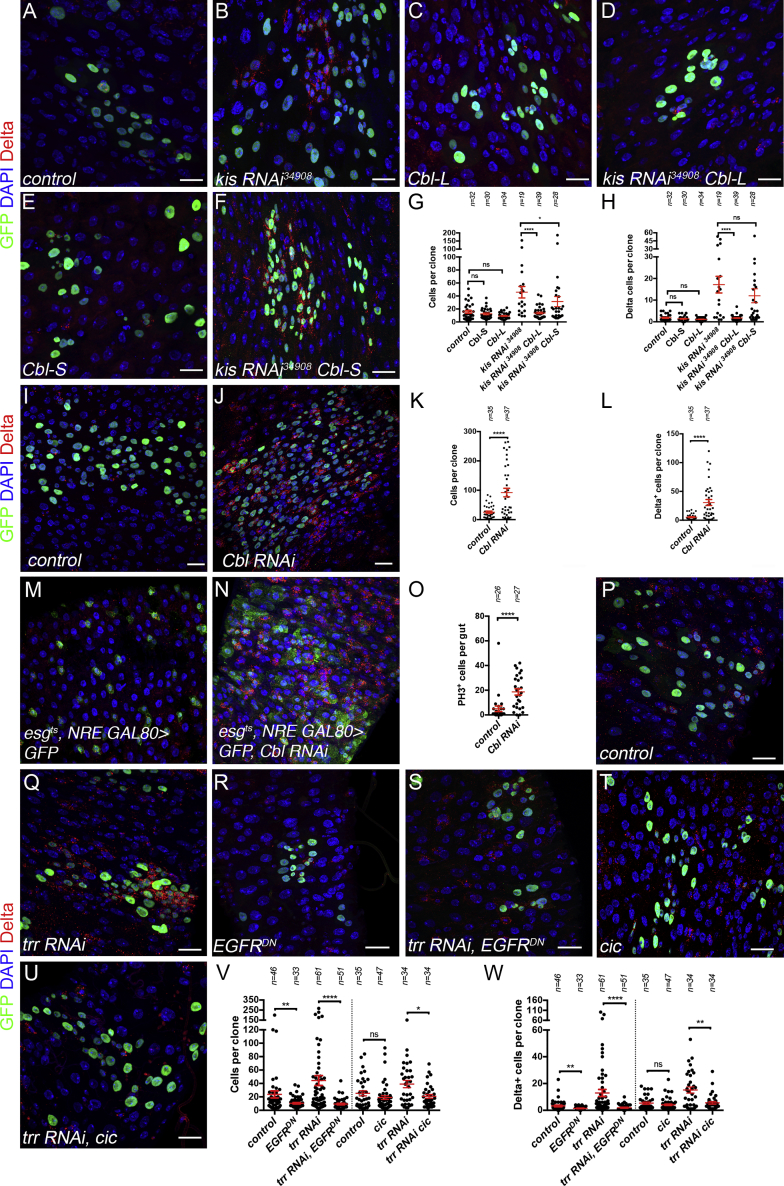
Figure 7.
Trr and Kismet Regulates EGFR Activity through the Control of Cbl Expression
(A–F) Clone of wild-type (A), kis RNAi34908 (B), UAS-Cbl-L (C), both kis RNAi34908 and UAS-Cbl-L (D), UAS-Cbl-S (E), and both kis RNAi34908 and UAS-Cbl-S (F) at 9 days AHS.
(G and H) Average number of cells and ISC per clone from (A)–(F).
(I and J) Clones of wild-type (I) and Cbl RNAi (J) 10 days AHS.
(K and L) Average number of cells and ISC per clone from (I) and (J).
(M and N) ISC-specific expression of GFP (M) and Cbl RNAi (N) driven by esgts- NRE-GAL80 for 10 days at 29°C. Cbl knockdown results in an accumulation of GFP, Delta+ cells.
(O) Quantification of number of PH3+ cells per gut from (M) and (N).
(P–U) Clone of wild-type (P), trr RNAi (Q), UAS-EGFRDN (R), both trr RNAi and UAS-EGFRDN (S), UAS-cic (T), and both trr RNAi and UAS-cic (U) at 10 days AHS.
(V and W) Clone size (V) and number of Delta+ per clone (W) from (P)–(U). Results were compared using a two-tailed Mann-Whitney statistical test. Mean values in red; error bars, SEM; n = non-significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001. Scale bars, 20 μm.