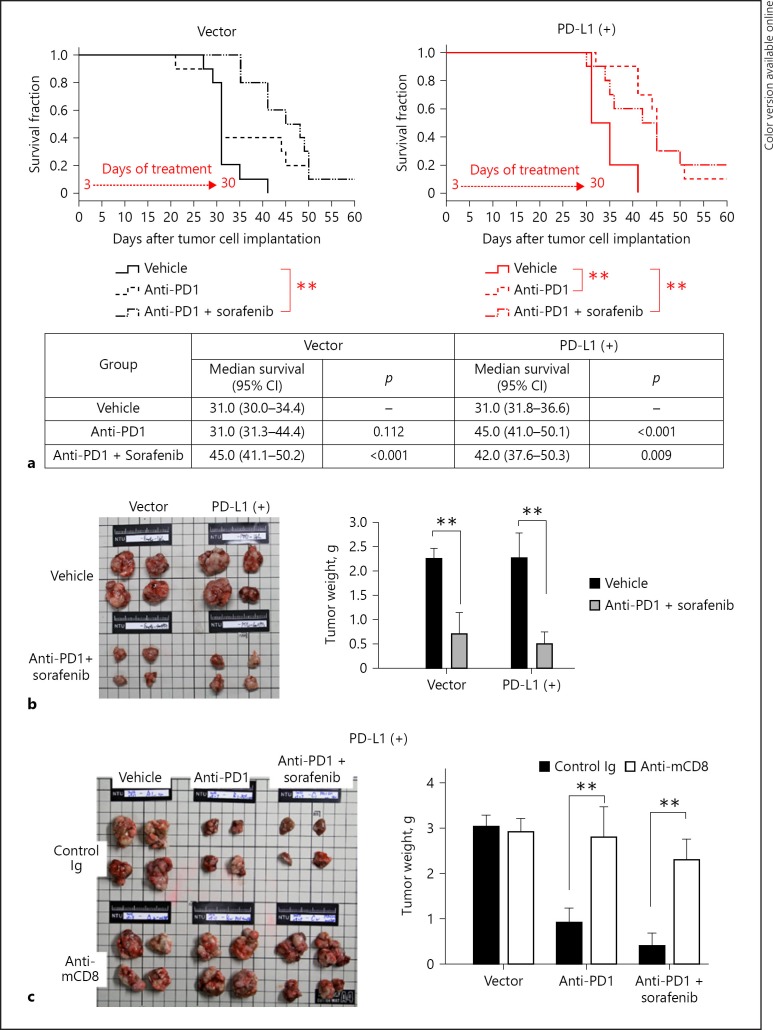
Fig. 6.
Antitumor efficacy of anti-PD1 plus sorafenib treatment. a Anti-PD1 therapy significantly improved survival only in mice with PD-L1-expressing tumors, while combination therapy was effective against both parental (vector) and PD-L1-expressing tumors. ** p < 0.01. b Combination of anti-PD1 therapy and sorafenib could reduce tumor size and weight in both PD-L1-expressing and parental tumors (n = 4 in each group). c The weight of PD-L1-expressing tumors treated with anti-PD1 therapy was significantly increased when the tumor was depleted of CD8+ T cells with anti-mouse CD8+ T cell antibodies (n = 5 in each group). Values are presented as means ± SD. was set at ** p < 0.01, statistically significant (one-way ANOVA).