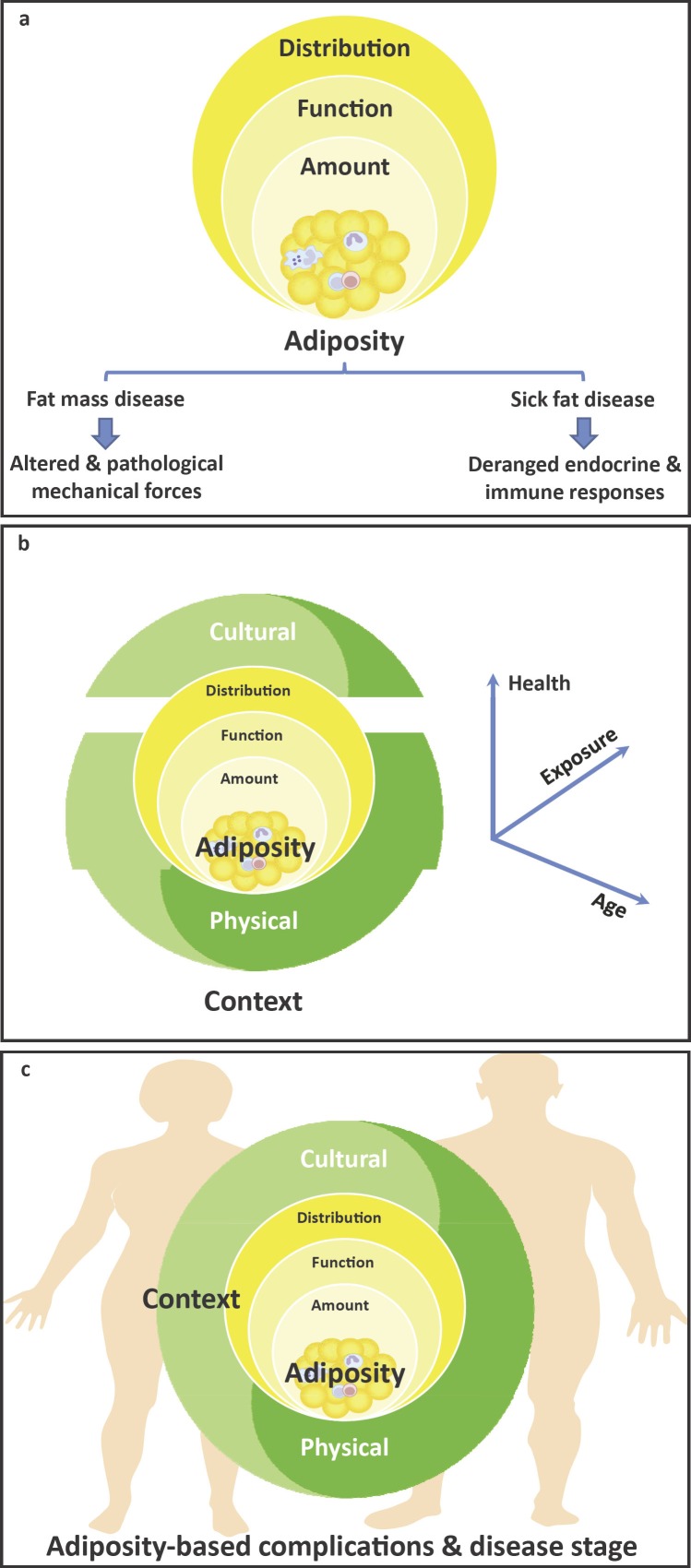
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of the adiposity-based chronic disease (ABCD) conceptual framework of obesity, which incorporates the characteristics of adiposity including the total amount, distribution, as well as function of adipose tissue (a), the physical (human-made or built environment, i.e., food availability, urban planning, endocrine disruptors, etc.) and cultural (socio-political-economic aspects, i.e., customs, attitudes towards food and physical activity, culture, ethnicity, beliefs, policy, inequalities, and stigmatization, among others) context in which it is embedded (b), together with the clinical burden derived from the impact of the dysfunctional fat over time, which leads to the development of complications and a gender-specific disease stage (c).