Fig. 1.
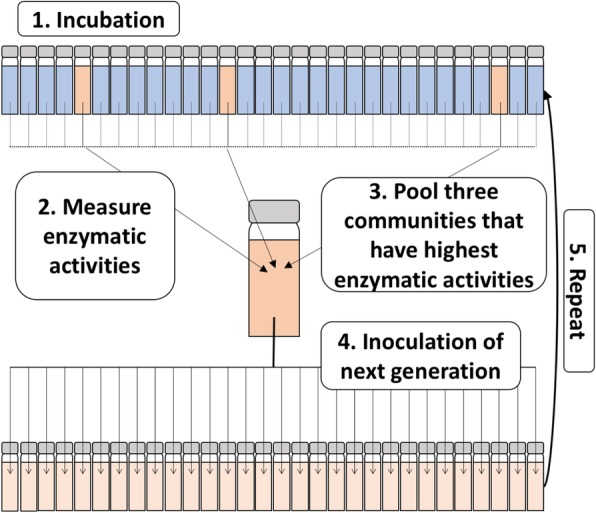
Method used for artificial selection of microbial communities. Briefly, 30 microcosms are inoculated with a natural community found in seawater (1). At the end of the incubation period, the enzymatic activity for a desired trait (e.g. chitinase activity) is measured for each microcosm (2). The three microcosms with the highest enzymatic activities are selected and pooled (3) and used to inoculate the next generation (4). This process is repeated over n generations (5)
