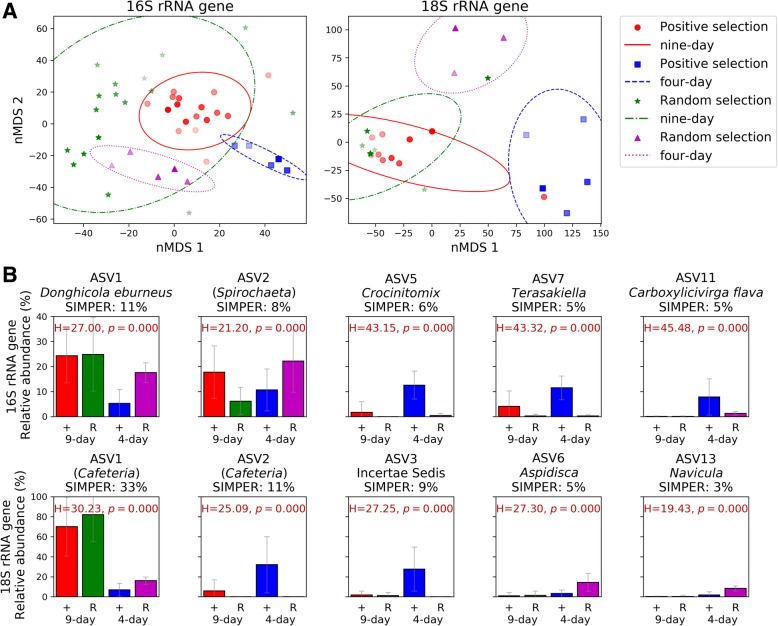
Fig. 5.
Microbial community variation over the entire artificial selection experiment. a nMDS plot showing Bray-Curtis distance of 16S (left) and 18S rRNA gene communities (right). Distance between the community composition obtained from 9-day (red circles) and 4-day incubations (blue squares) of the positive selection, and 9-day (green stars) and 4-day incubations (purple triangles) of the random controls are shown. The marker colour intensity correlates to the generation number, where progressive darker colours represent later generations. Each point represents the mean of the three communities selected from one generation used to inoculate the following one, for the positive selection. Random communities were pooled before sequencing. Ellipses show the mean plus the standard deviation of each group of samples. Stress values are 0.175 for the 16S rRNA gene and 0.063 for the 18S rRNA gene. b Five 16S (top panel) and 18S rRNA gene ASVs (bottom panel) that contributed the most towards community variations between the 9-day (generations 0–20) and 4-day (generations 16–20) positive (+) and random (R) selections according to SIMPER analyses. The percentage of variation to which each ASV contributes is indicated. ASVs were classified to the species level with the standard analysis pipeline using the SILVA database (v132) where possible. Names in brackets were not identifiable and were identified through a BLAST search of the NCBI database. Relative abundances and error bars shown are the mean and standard deviations of all generations within that treatment