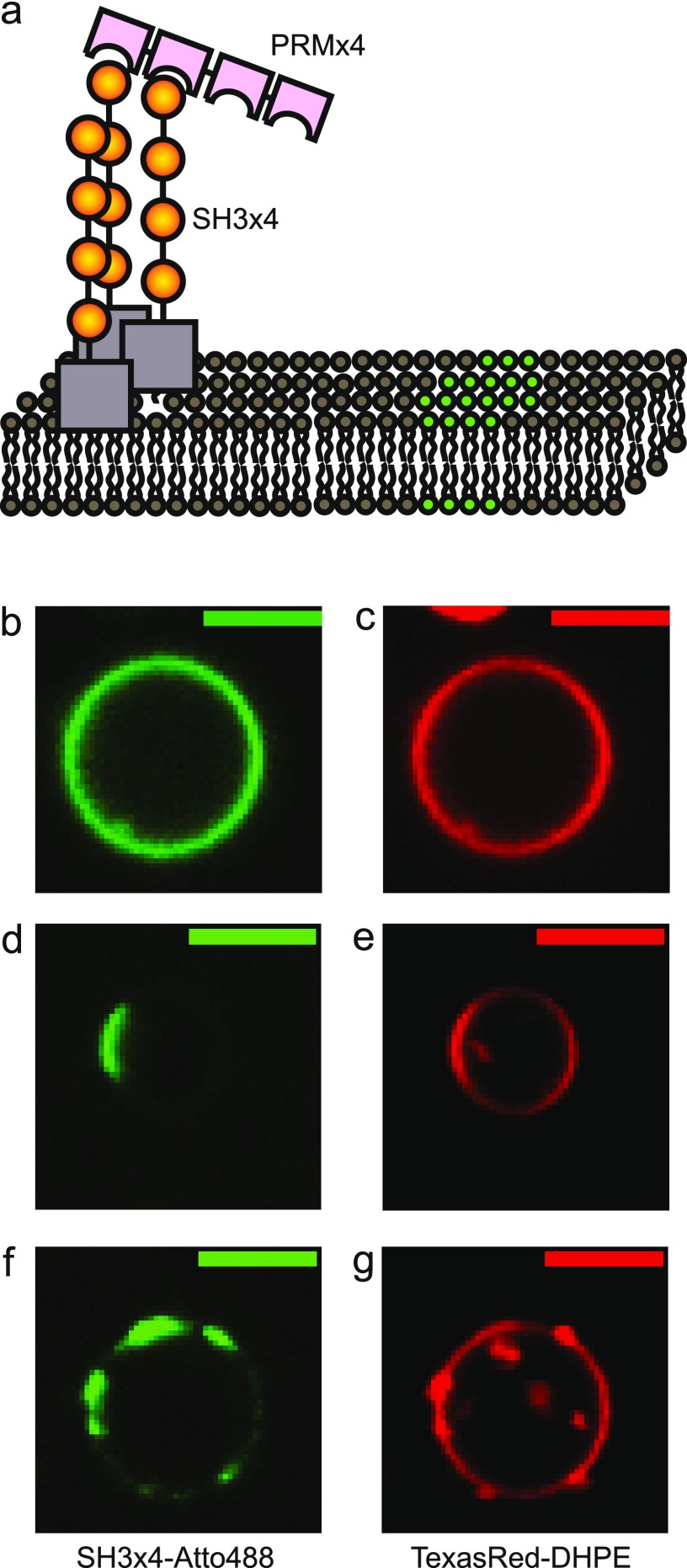
Figure 2.
Two-component phase-separating proteins on the phase-separated lipid membrane. (a) SH3 × 4 and PRM × 4 were added from solution to interact with ternary mixture GUVs with phase separation properties (green and gray for separated domains). SH3 × 4 (yellow) had a small soluble maltose binding protein (MBP, gray) domain with a polyhistidine tag, so it spontaneously anchored itself to the membranes by strong binding to Ni-NTA lipid. (b, c) Matching typical images of the Atto488 protein channel and the TexasRed-DHPE lipid channel of a two-phase-separated GUV. (d, e) Matching typical images of a two-phase-separated GUV. (f, g) Matching typical images of a GUV with multiple-phase domains. Scale bars are 5 μm. Lipid compositions were 45% DOPC, 20% DPPC, 35% cholesterol, 5% DOPS, 10% Ni-DGS, 0.1% TR-DHPE.